AnalyzeDynamicLightScattering
AnalyzeDynamicLightScattering[DynamicLightScatteringData]⟹Object
Calculates the key scientific parameters derived from the dynamic light scattering protocol, including Z-average diameter, second virial coefficient (b22), diffusion interation parameter (kD), and Kirkwood Buff integral (G22).
AnalyzeDynamicLightScattering[DynamicLightScatteringProtocol]⟹Object
Analyzes all the data in the given protocol.
AnalyzeDynamicLightScattering[MeltingCurveData]⟹Object
Calculates the Z-average diameter, polydispersity index, and diffusion coefficient for MeltingCurve data objects generated from Object[Protocol, ThermalShift].
Details
- Two particle sizing methods are available: the instrument calculation and the cumulants method based on International Organization of Standardization (ISO) 22414:2017
- The cumulants method fits the decaying correlation curves with a single exponential that contains a polynomial in the exponent. Regarding the polynomial, the first order term represents the mean particle size, the second represents the variance, the third represents the skewness.
- Correlation curves can be excluded from the analysis if their initial values are too low, indicating improper sample loading, or if the correlation curve does not converge near 0, indicating significant noise.
- The diffusion coefficient is estimated by regressing the diffusion coefficient versus protein concentration. The ratio of the slope to y-intercept is the diffusion interaction parameter.
- The second virial coefficient is estimated by regressing the optical constant times the concentration divided by the Rayleigh ratio versus concentration. Half of the slope is the second virial coefficient.
- The Kirkwood Buff integral is estimated by regressing the Rayleigh ratio divided by the optical constant versus a first and second order coefficient term. The coefficient to the second order term divided by the molecular weight is the Kirkwood Buff integral.
Input

Output

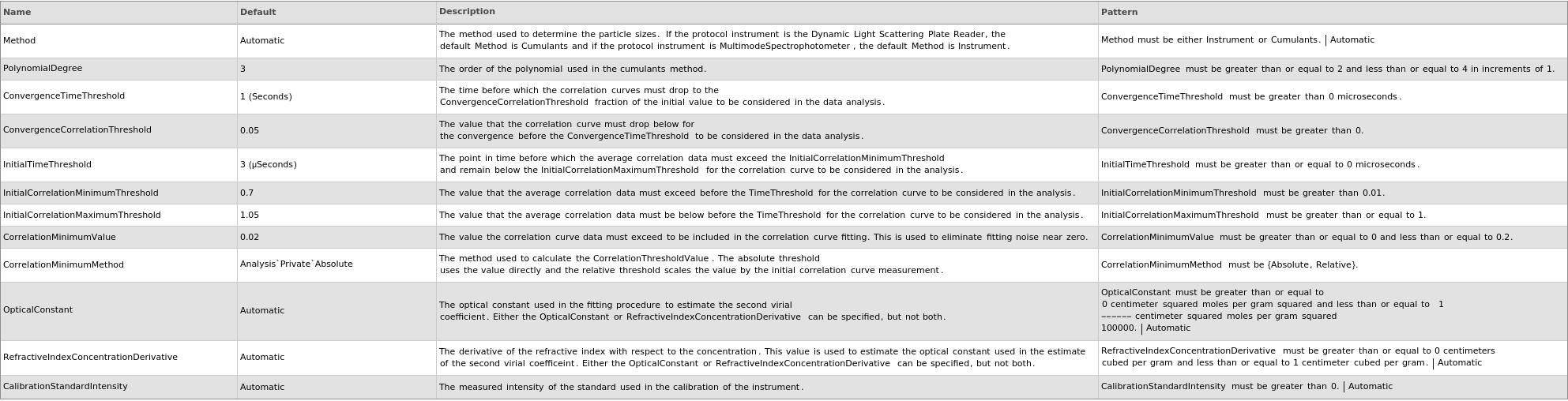
General Options
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Additional Examples (12)
Analyze all data within a DynamicLightScattering Protocol:
Analyze melting curve data to create an Analysis Object:
For AssayType B22kD, calculate the PolyDispersityIndices using the cumulants method:

For AssayType G22, calculate the Kirkwood-Buff Integral:
For AssayType G22, calculate the Z-average diameter using the cumulants method:
For AssayType G22, create analysis objects of all data in the protocol:
For AssayType IsothermalStability, calculate the DiffusionCoefficients:
For AssayType IsothermalStability, calculate the ZAverageDiameters using the cumulants method:
For AssayType IsothermalStability, create analysis objects of all data in the protocol:
For AssayType SizingPolydispersity, calculate the zAverageDiameters:
For AssayType SizingPolydispersity, calculate the zAverageDiameters using the cumulants method:
For AssayType ThermalShift, calculate the ZAverageDiameters using the cumulants method: