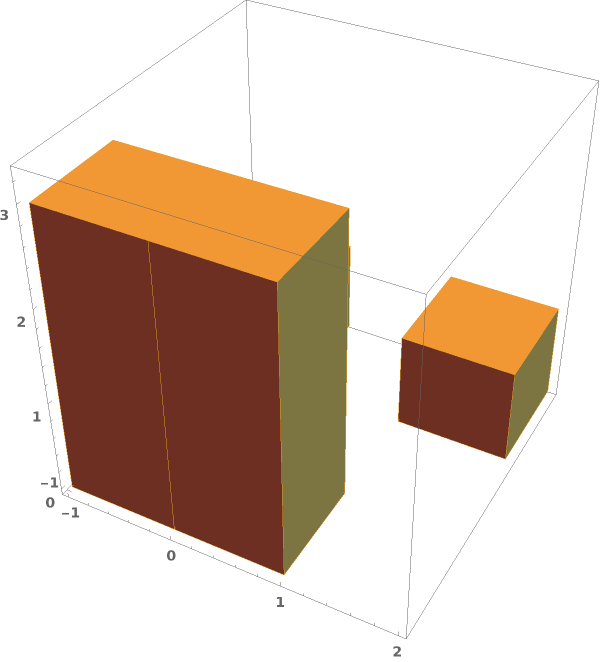
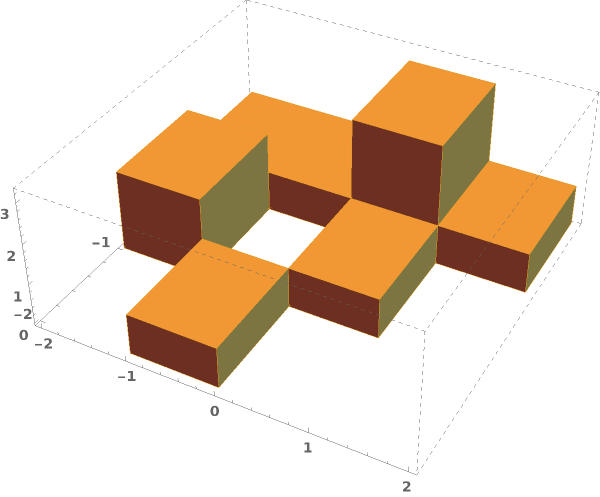
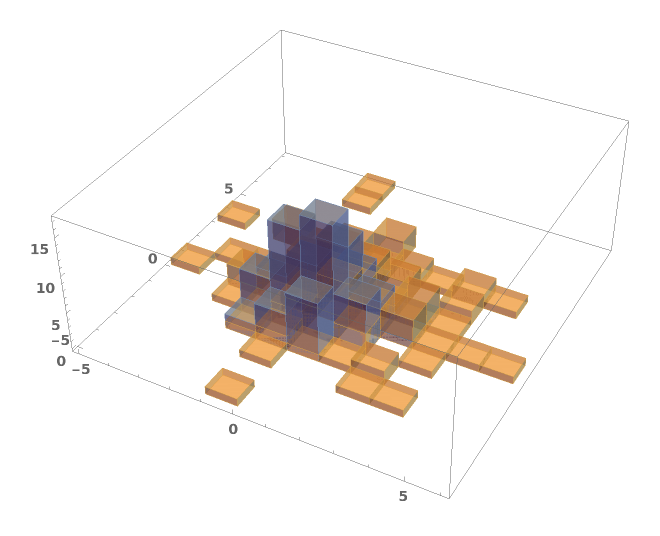
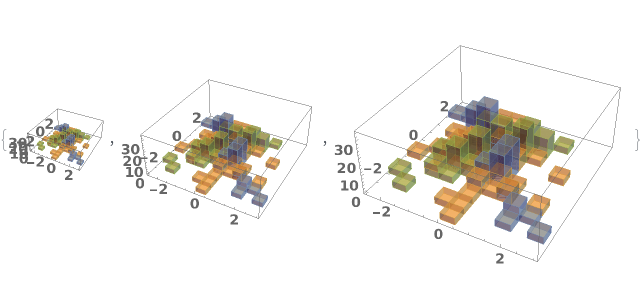
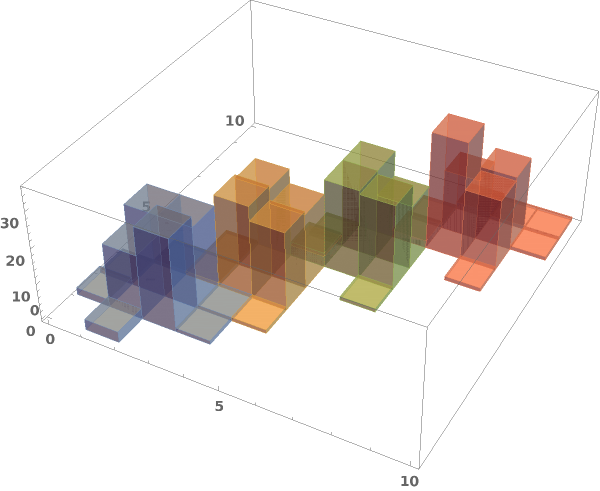
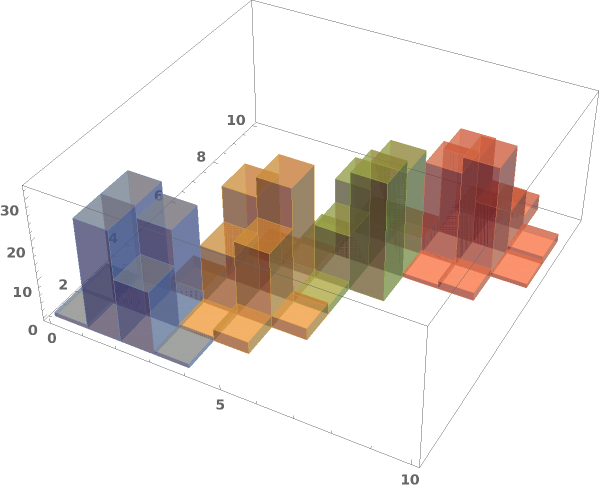
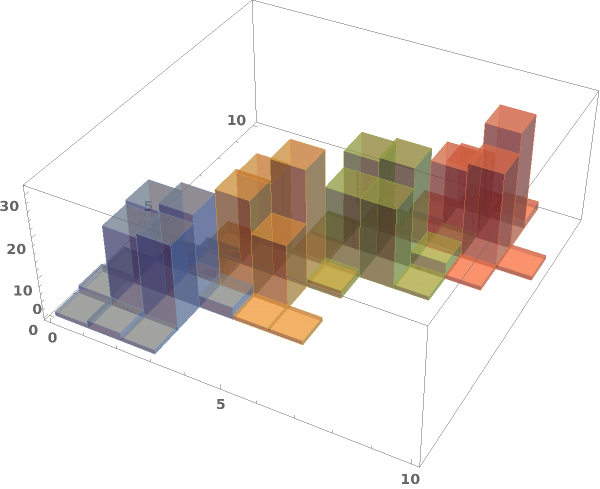
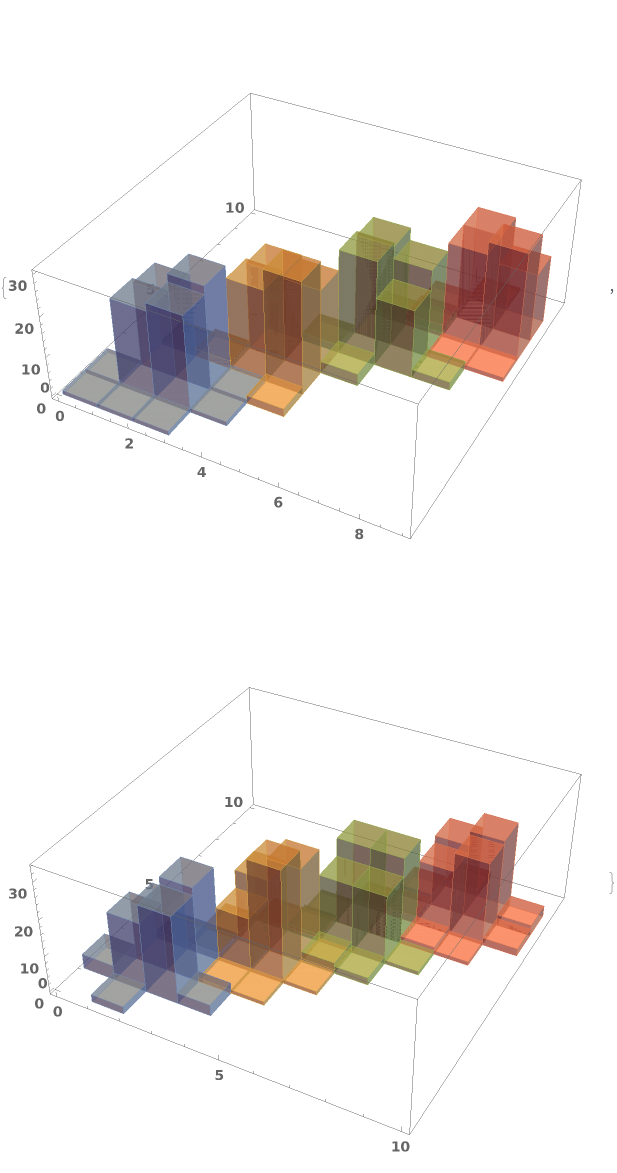
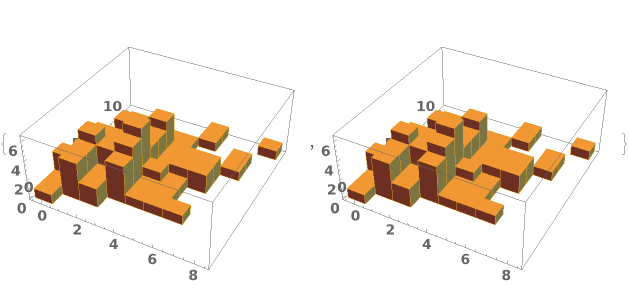
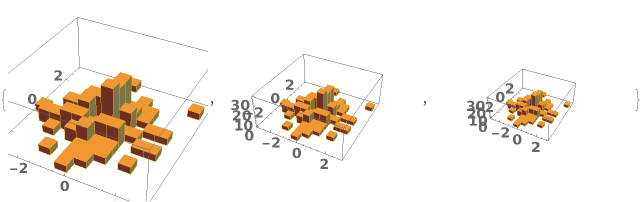
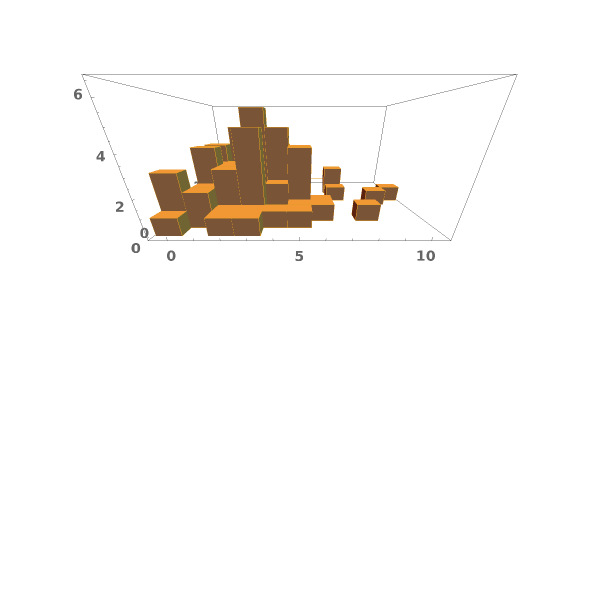
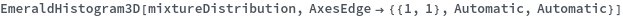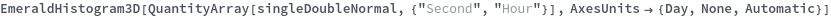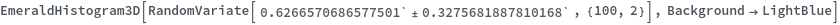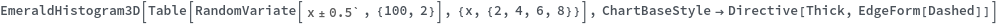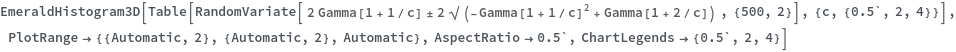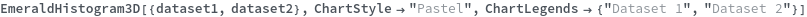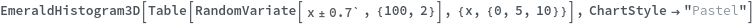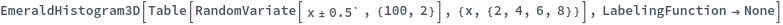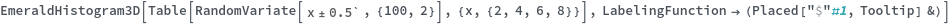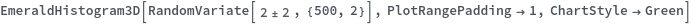EmeraldHistogram3D
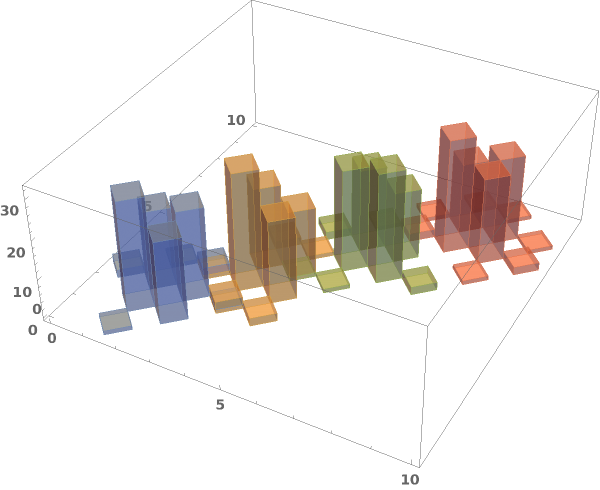
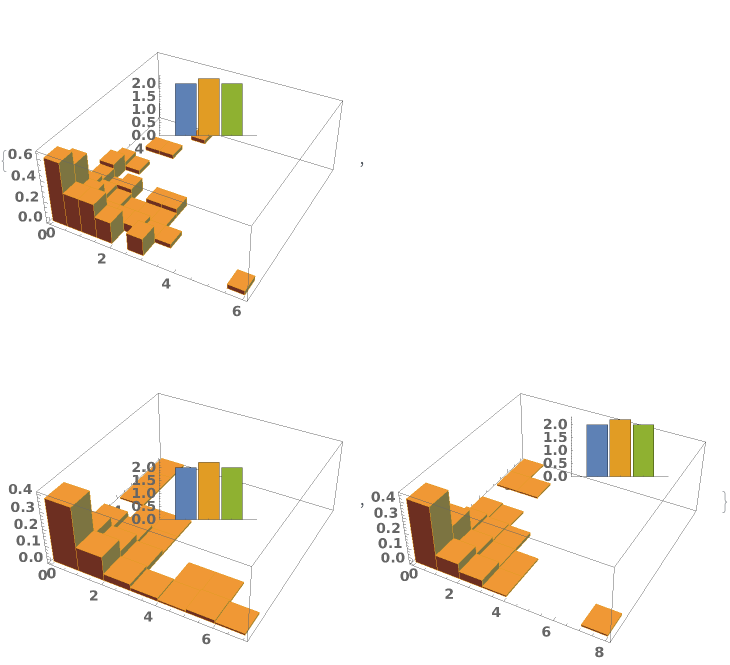
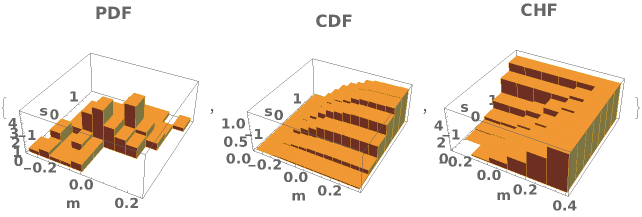
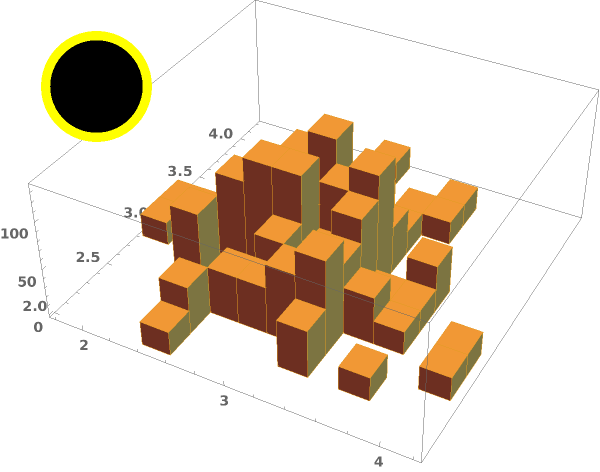
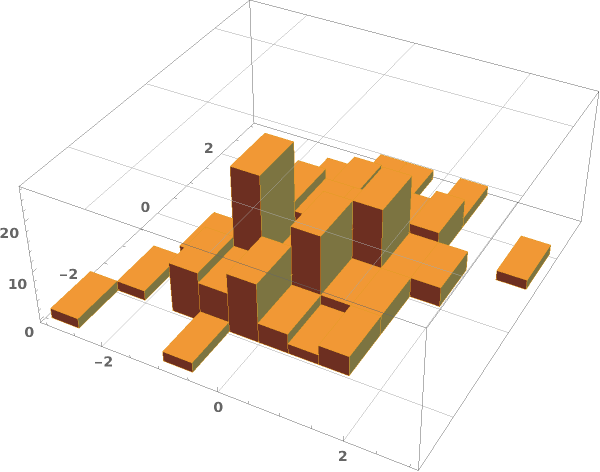
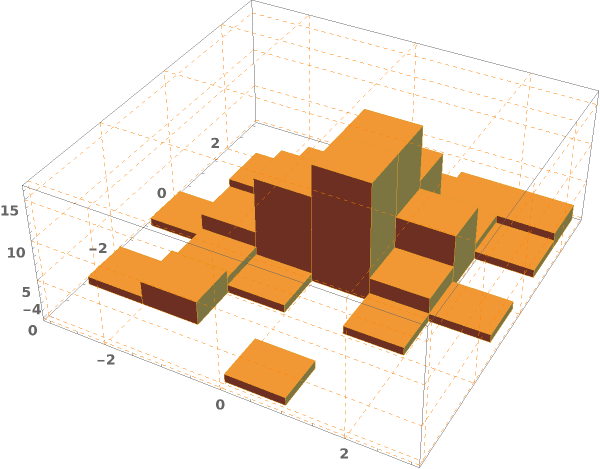
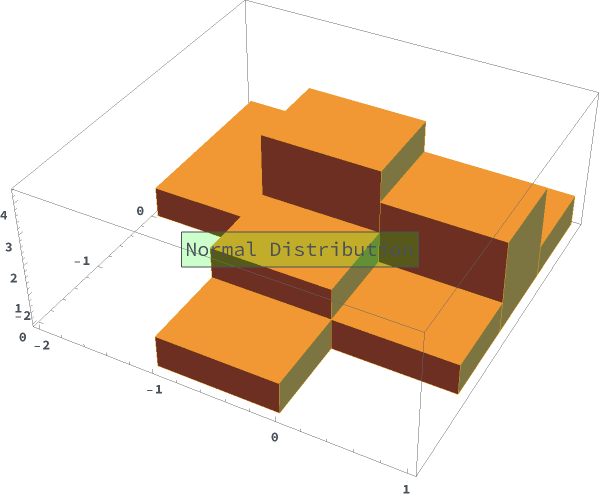
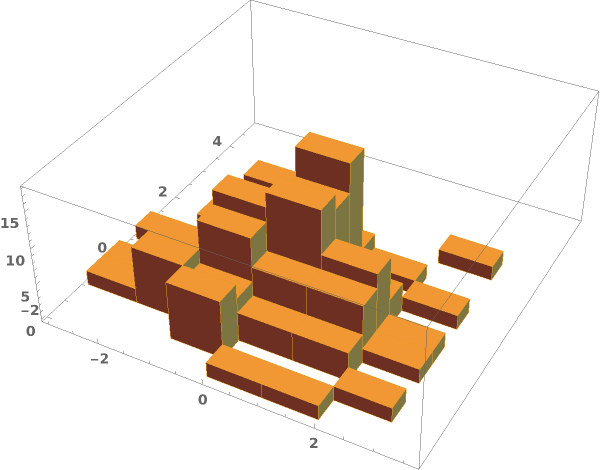
EmeraldHistogram3D[dataset]⟹chart
creates a Histogram3D from the provided dataset.
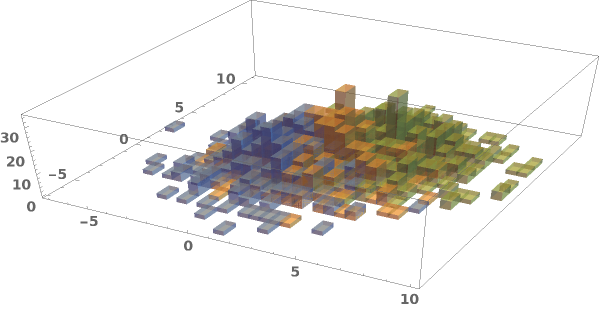
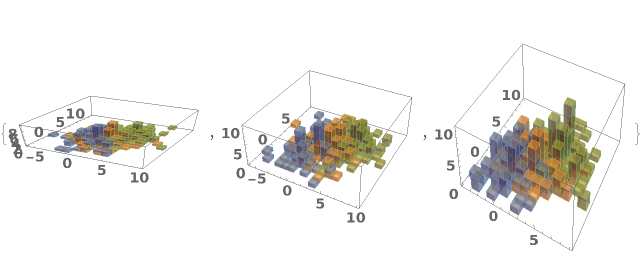
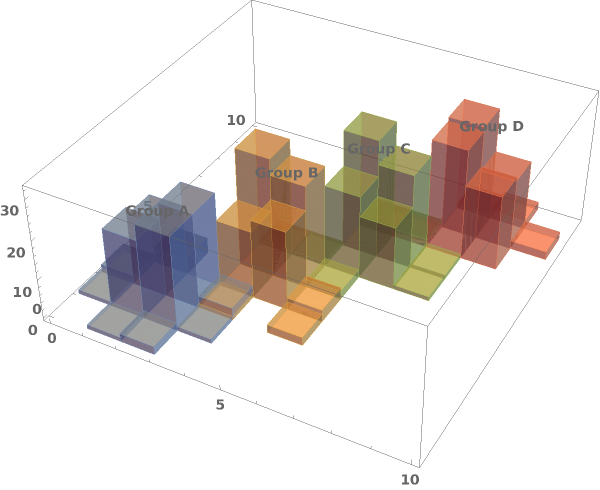
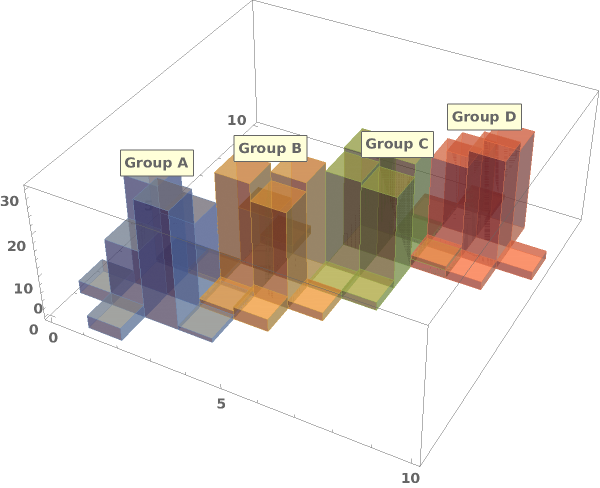
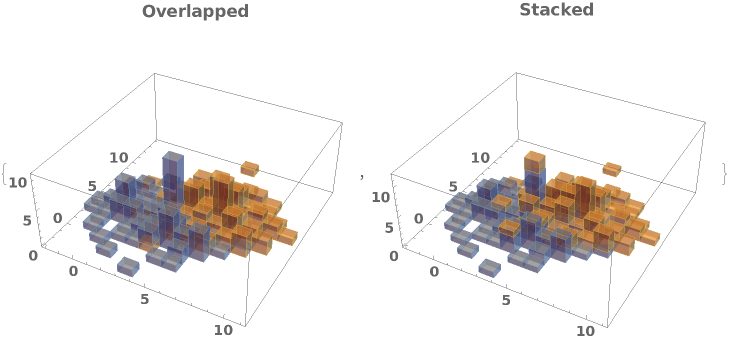
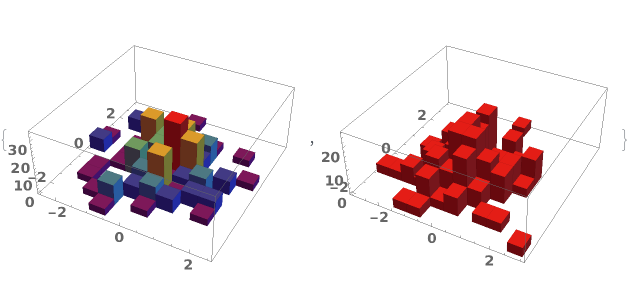
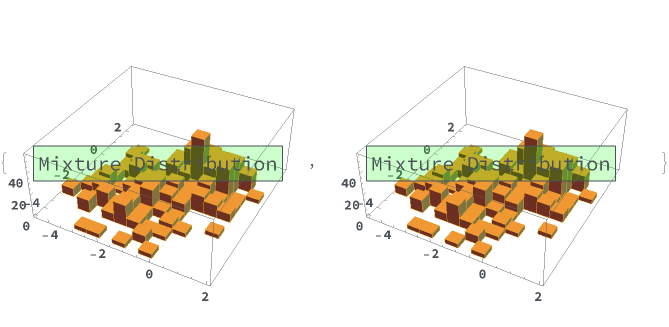
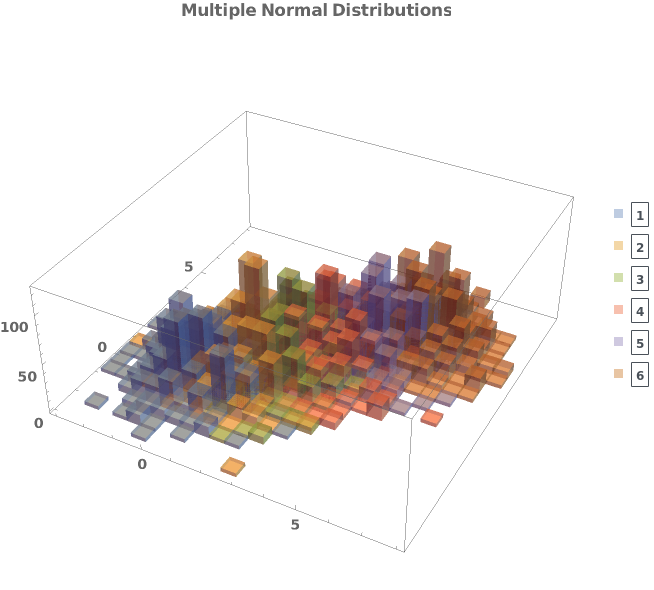
EmeraldHistogram3D[datasets]⟹chart
creates a Histogram3D displaying each input dataset in datasets.
Details
Input
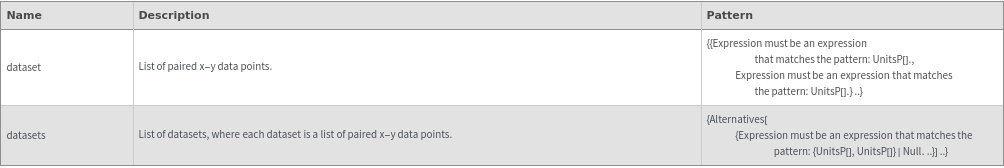
Output

3D View Options
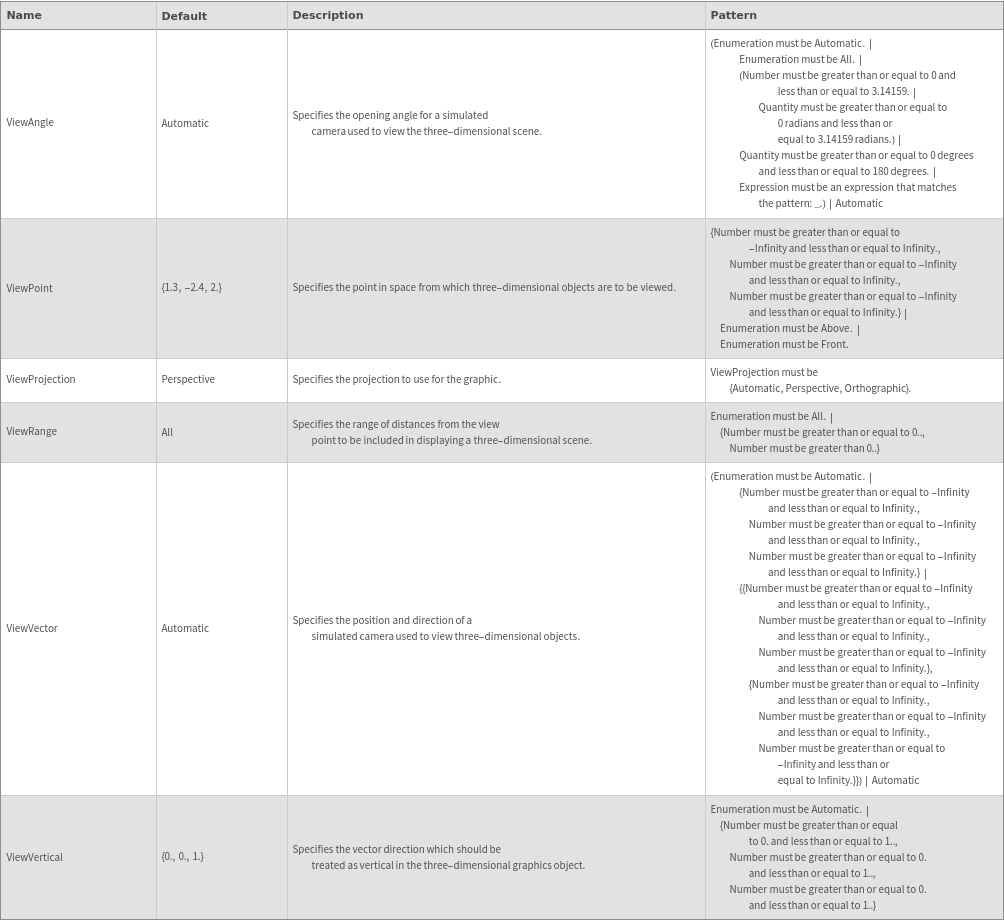
Axes Options
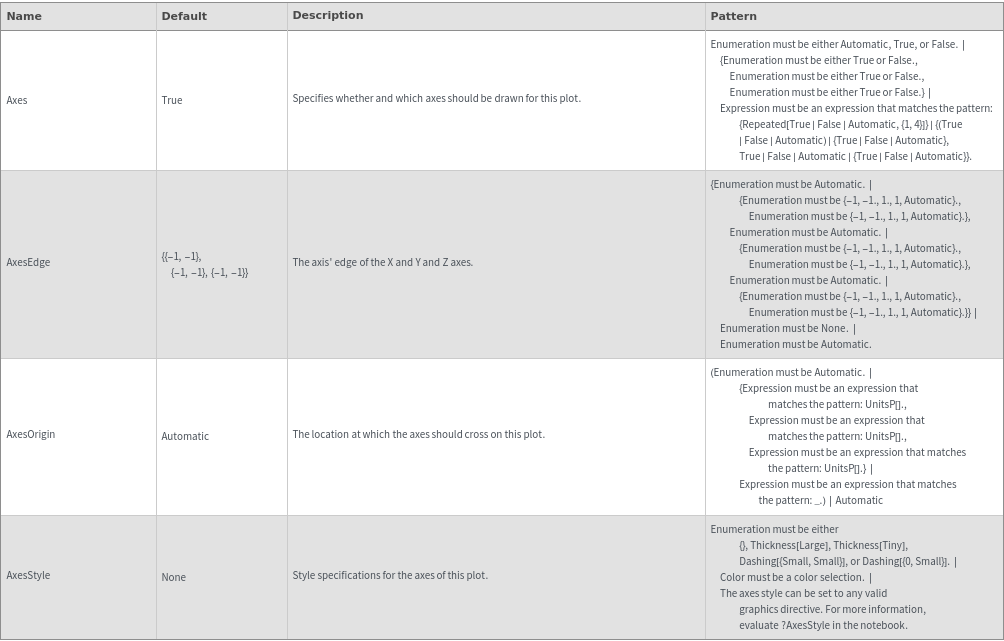
Box Options
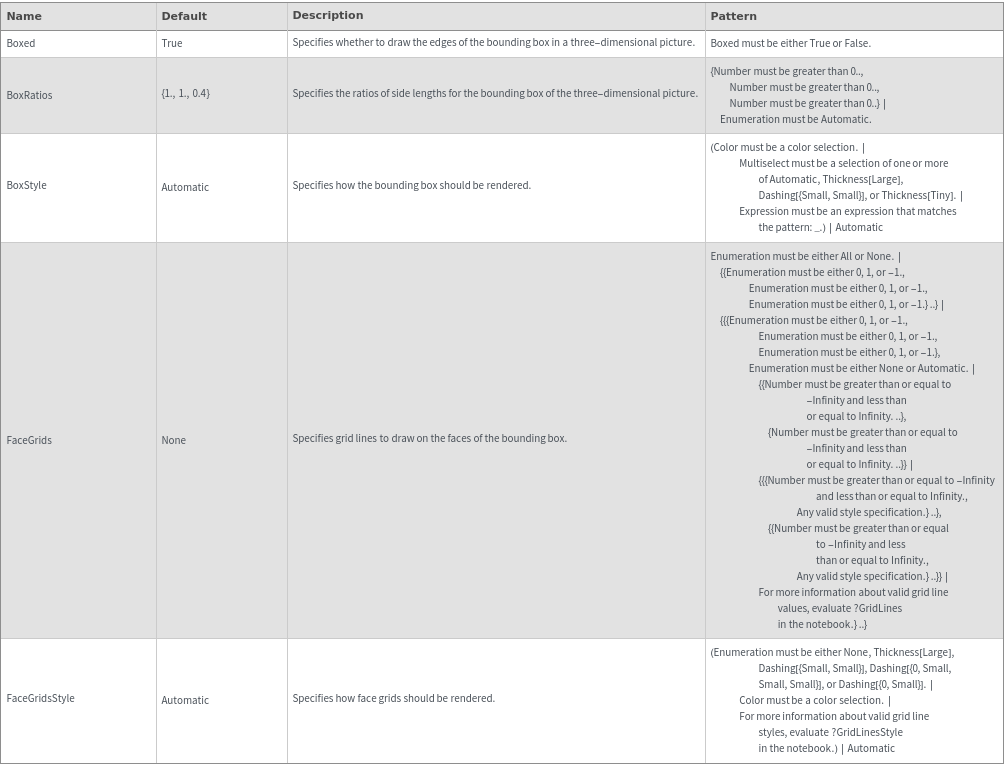
Data Specifications Options
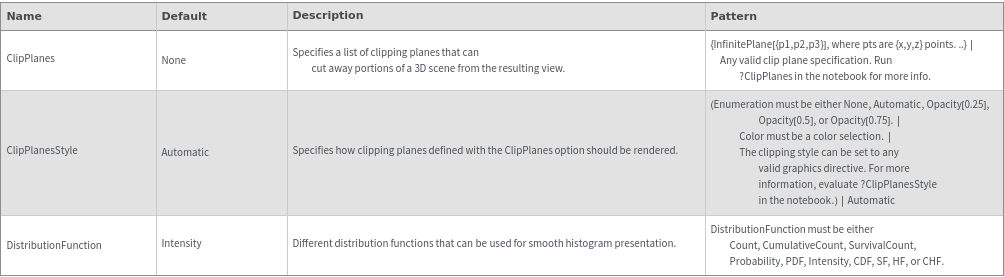
Image Format Options
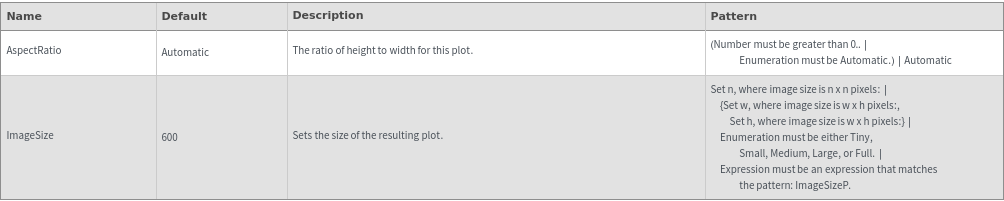
Legend Options
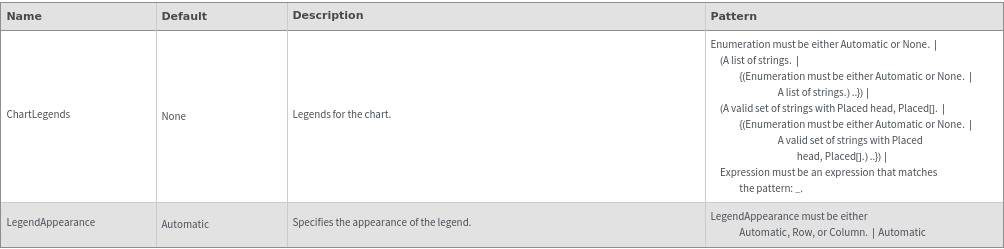
Plot Labeling Options
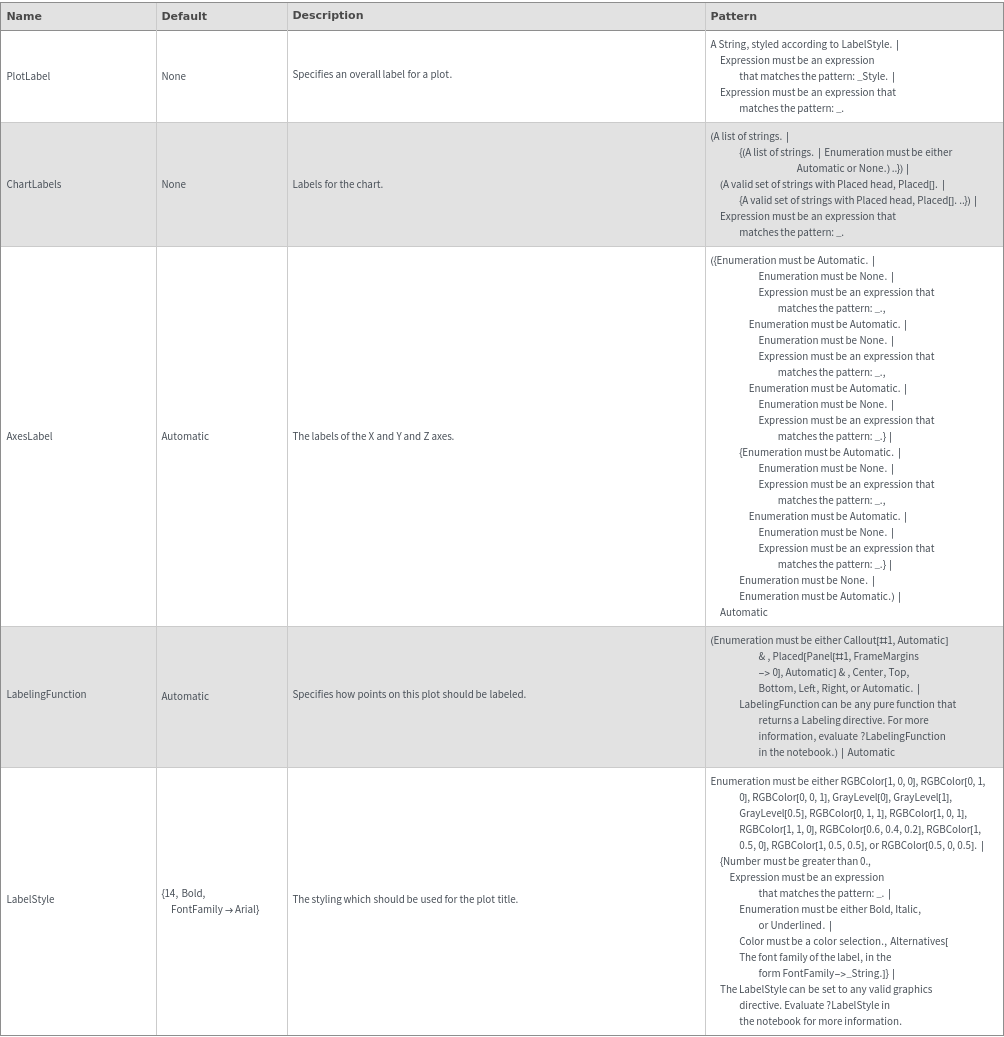
Plot Range Options
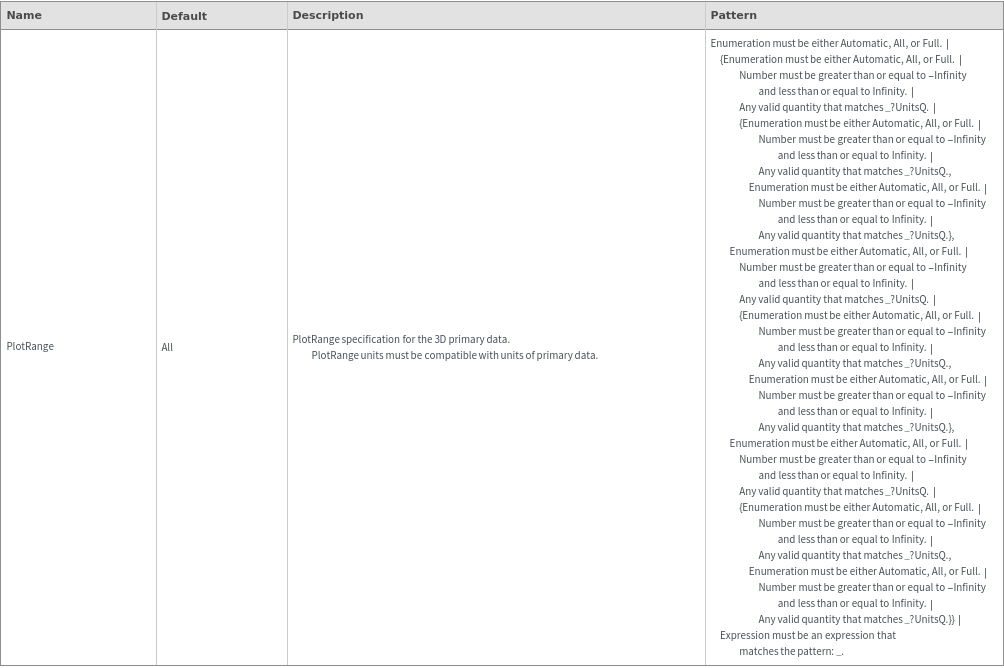
Plot Style Options
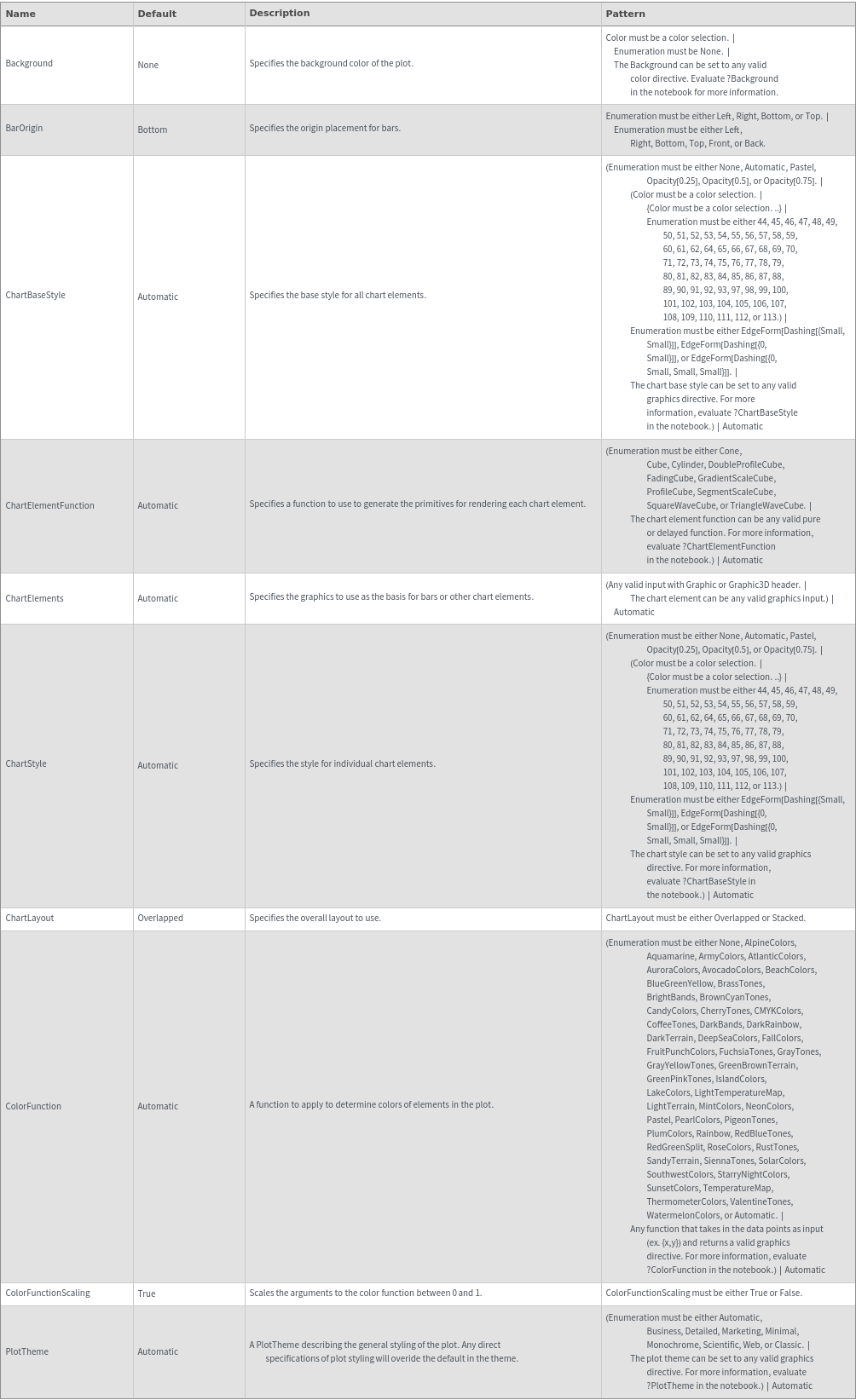
General Options

Examples
Basic Examples (3)
Options (70)
AlignmentPoint (1)
AxesEdge (1)
AxesUnits (2)
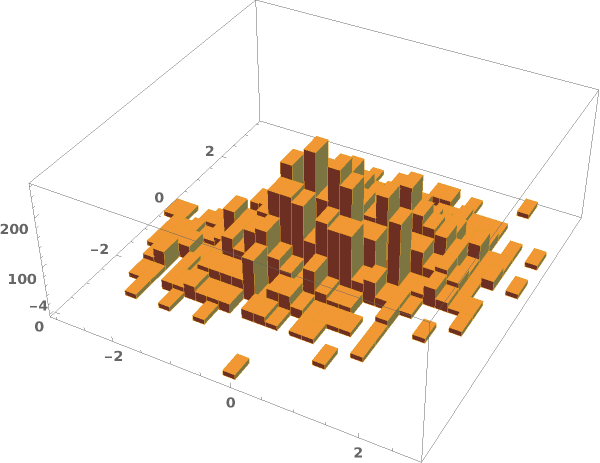
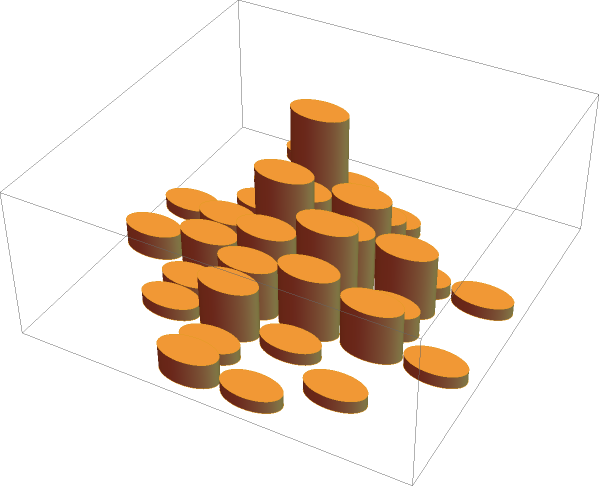
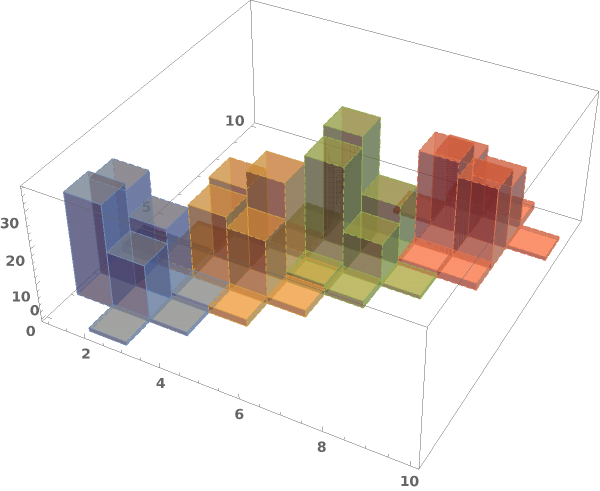
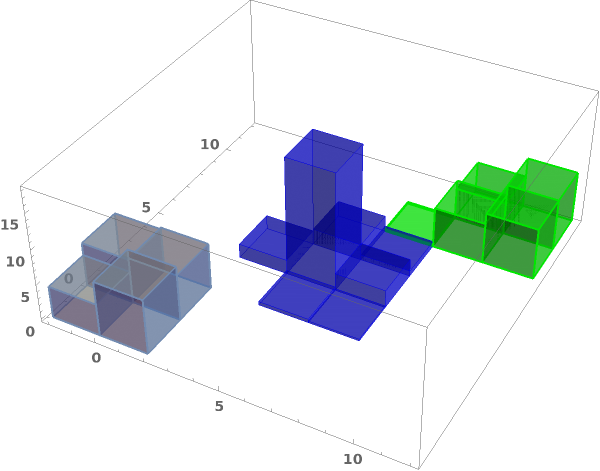
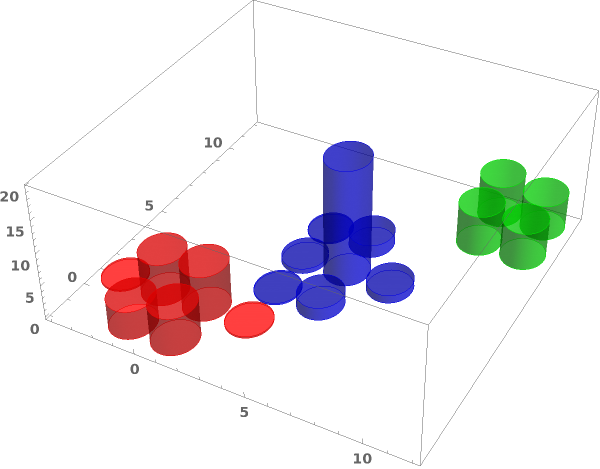
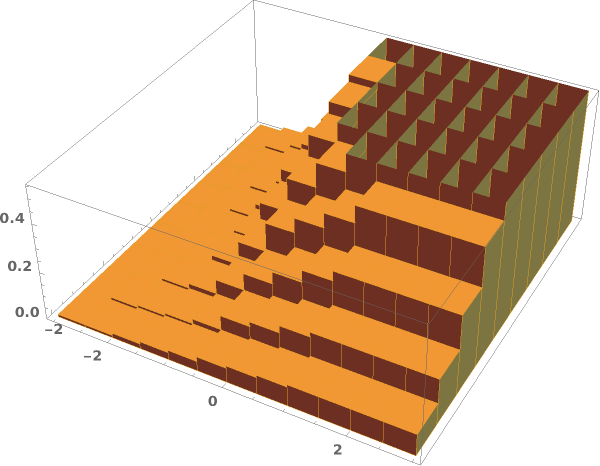
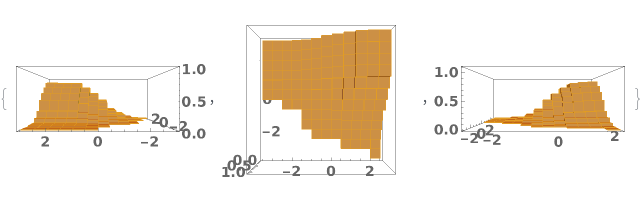
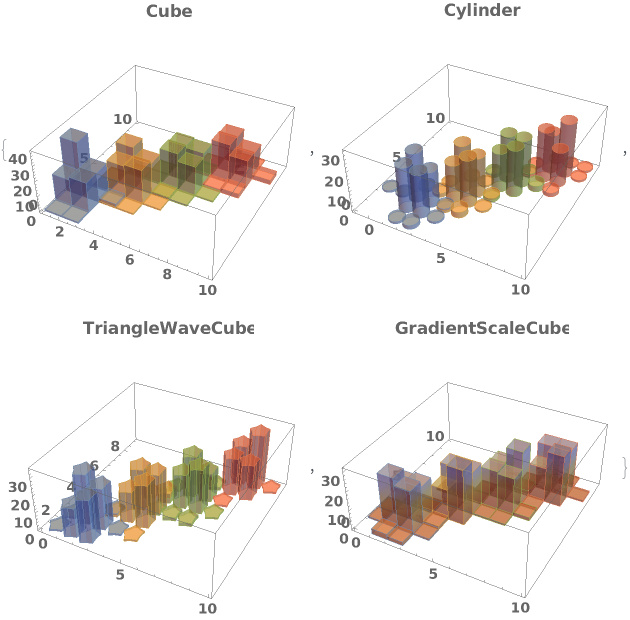
ChartElementFunction (4)
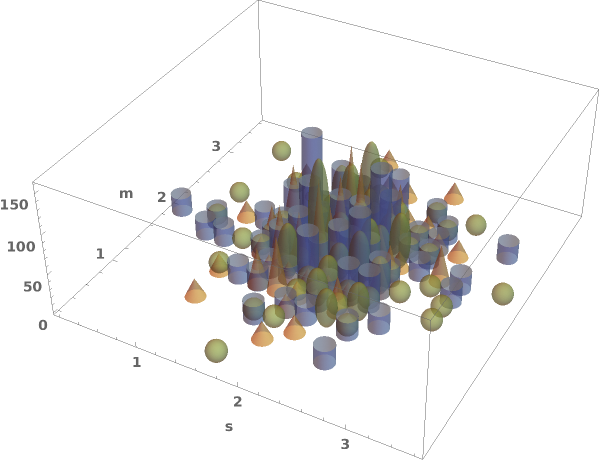
Choose a chart element function from a list of presets, which can be viewed by running ChartElementData["Histogram"] in the notebook. Automatic defaults to "Cube":

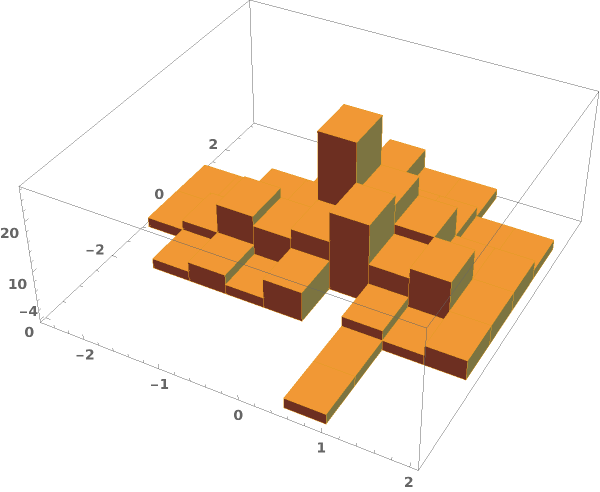
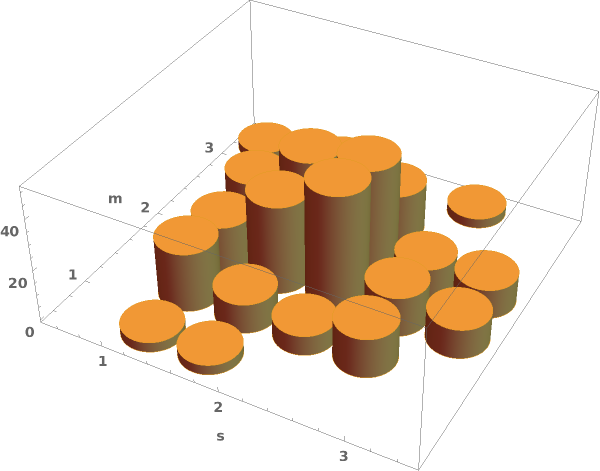
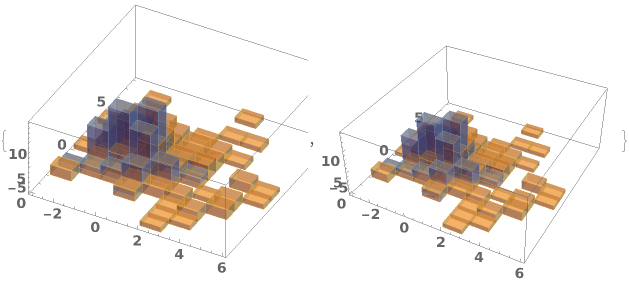
Write a custom ChartElementFunction:
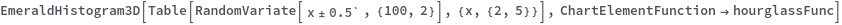
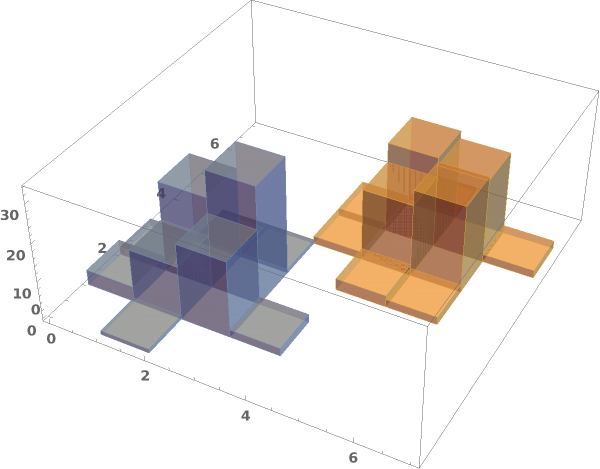
Write a custom ChartElementFunction:

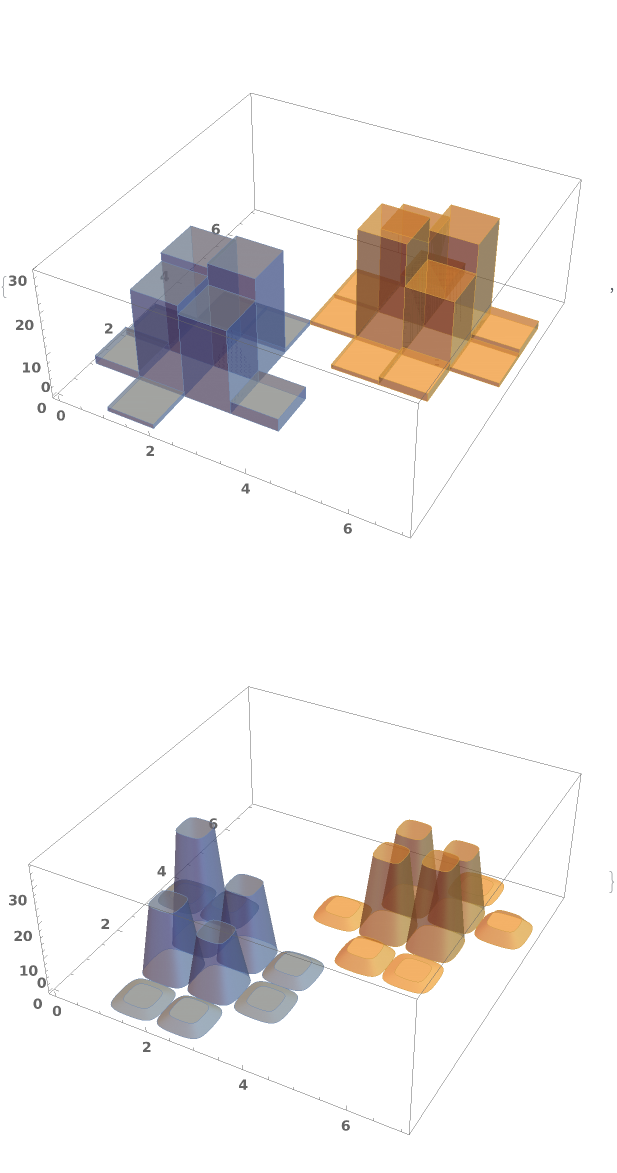
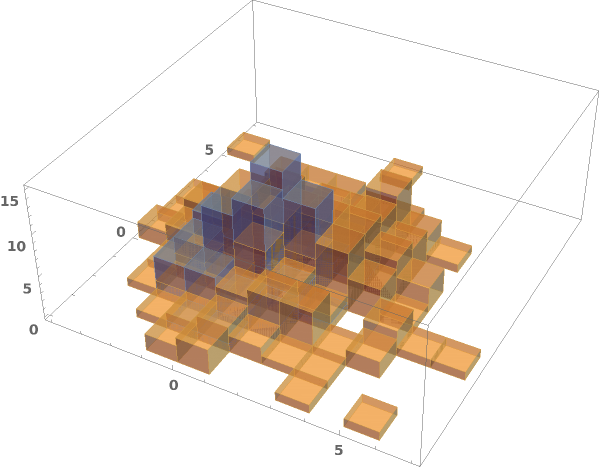
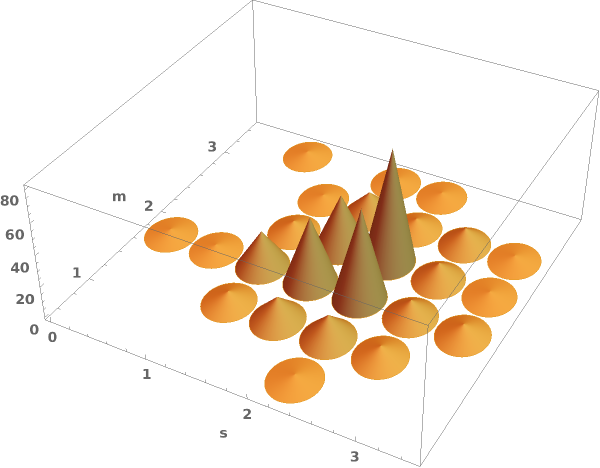
Some built-in chart element functions take options. As an example, you can view the options for the default Rectangle function by running ChartElementData["Histogram3D"] in the notebook: