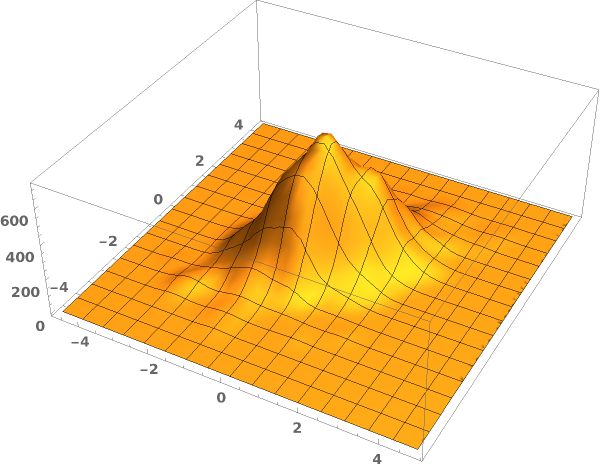
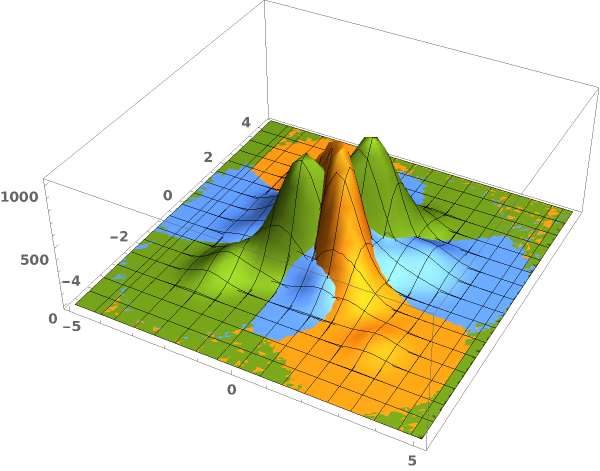
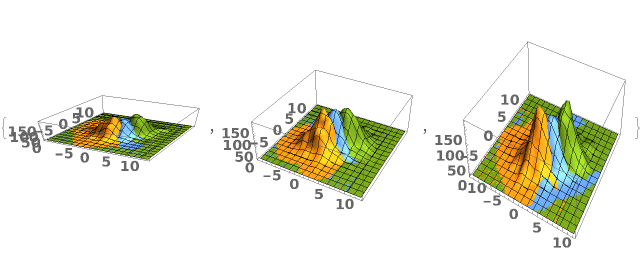
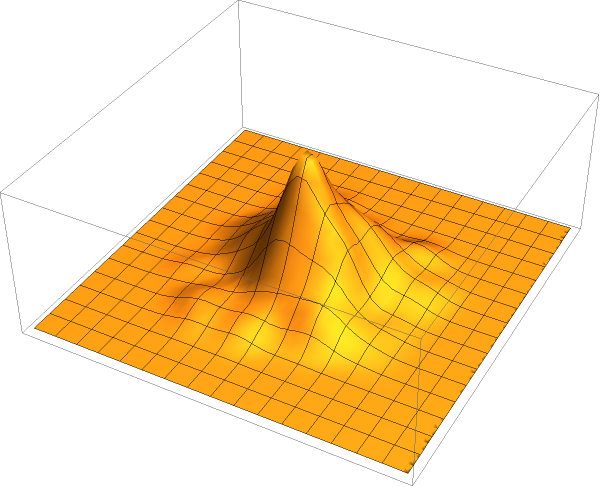
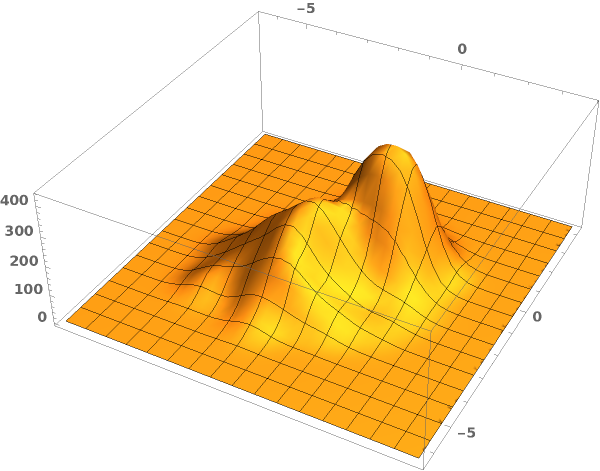
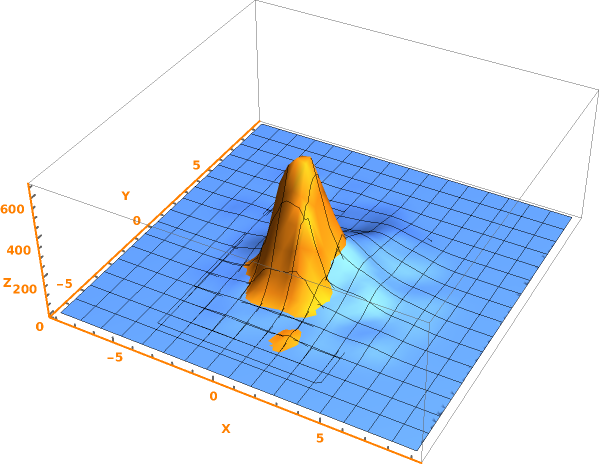
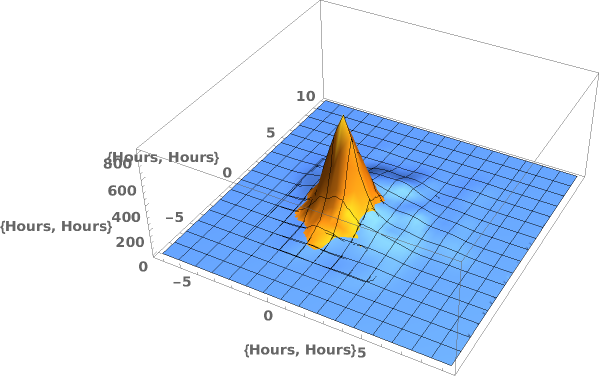
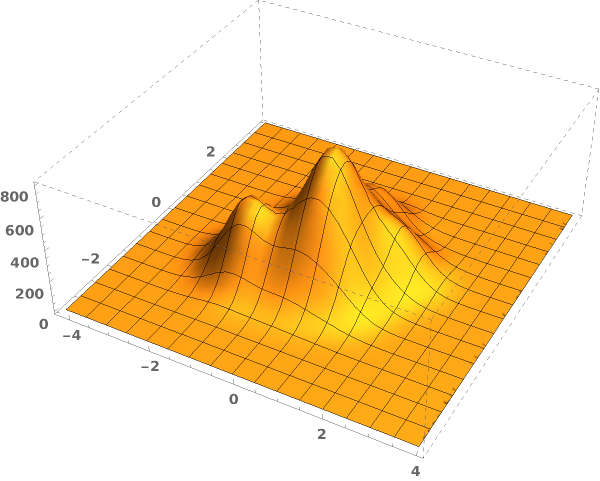
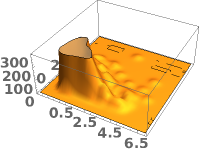
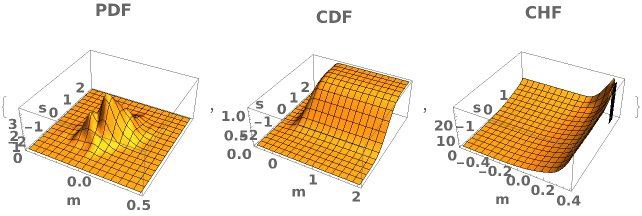
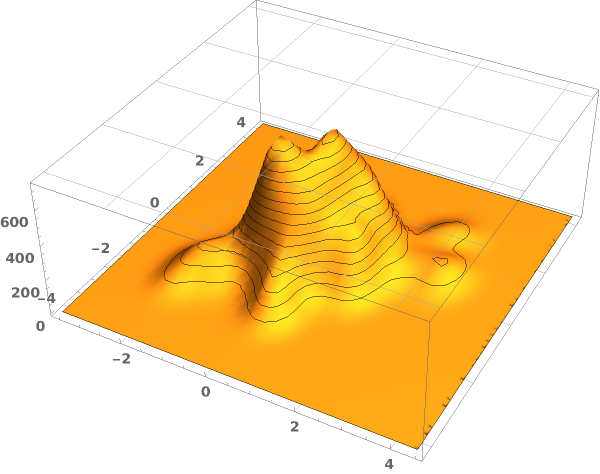
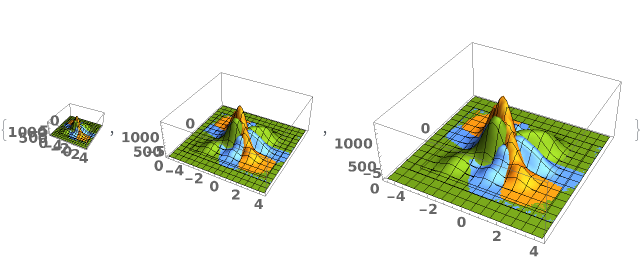
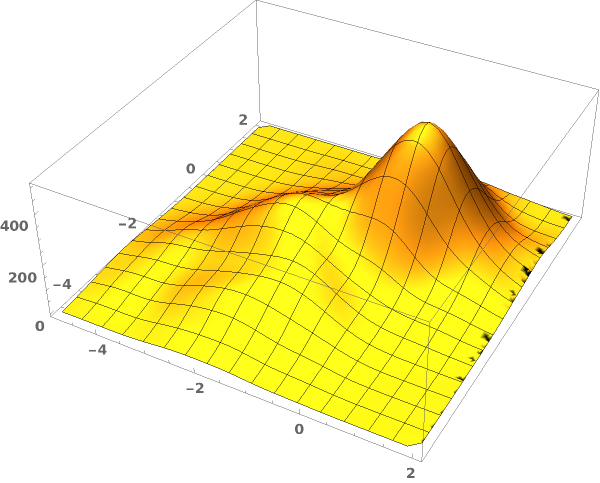
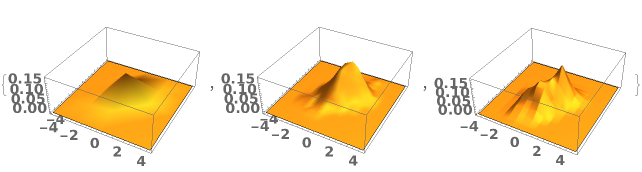
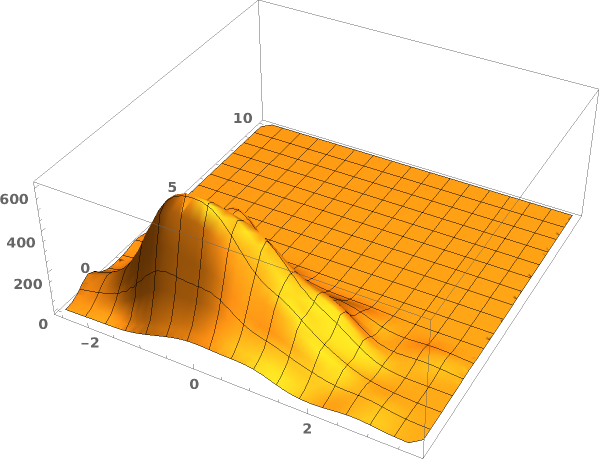
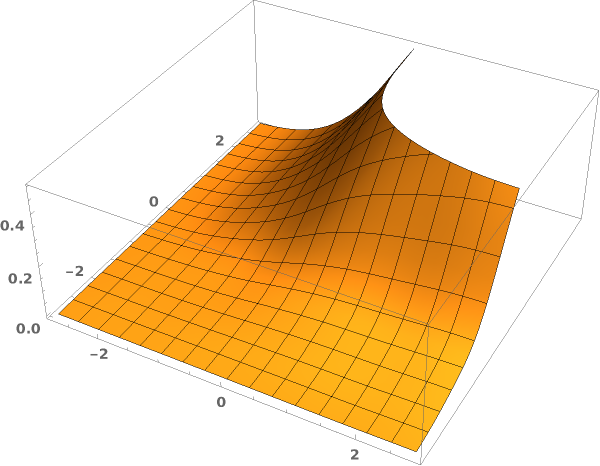
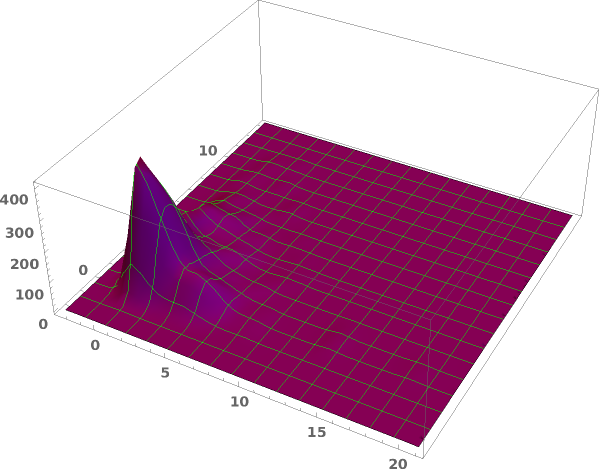
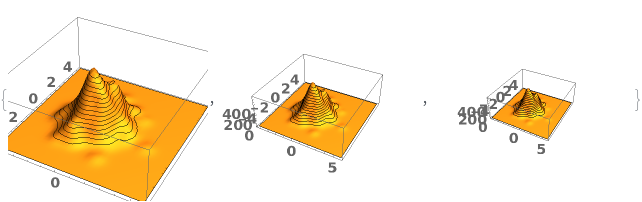
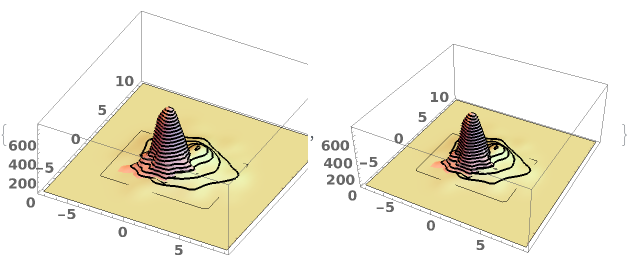
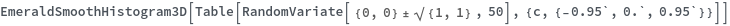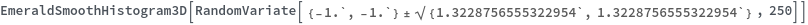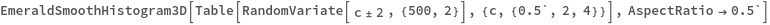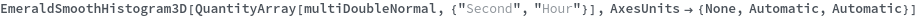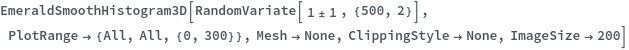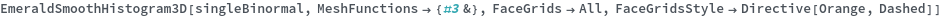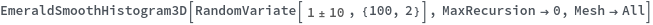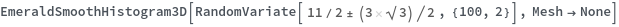EmeraldSmoothHistogram3D
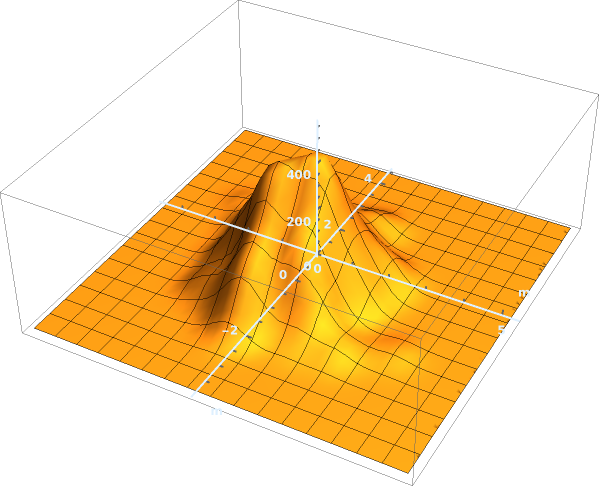
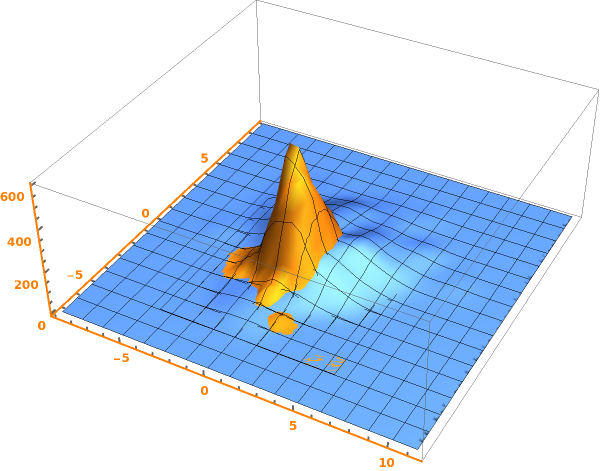
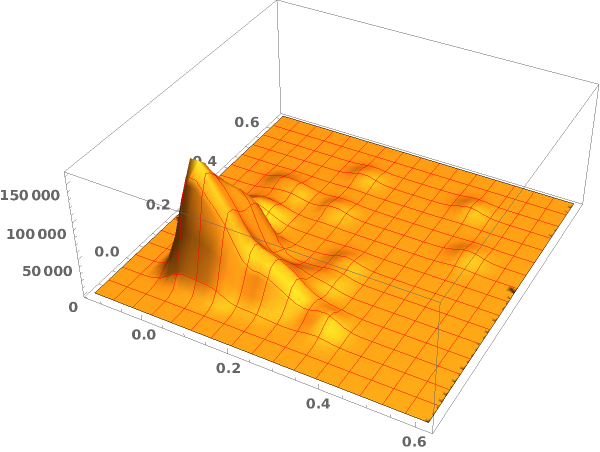
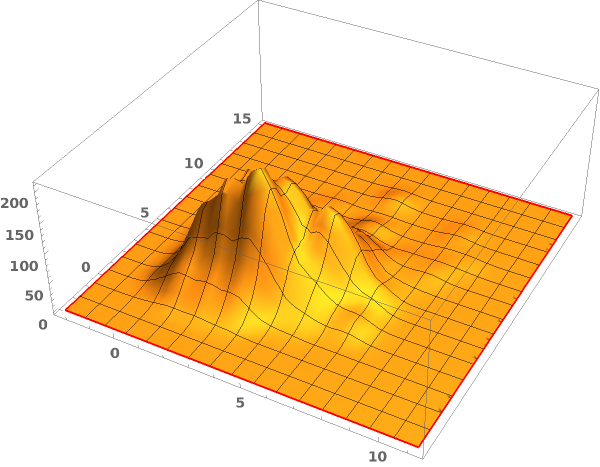
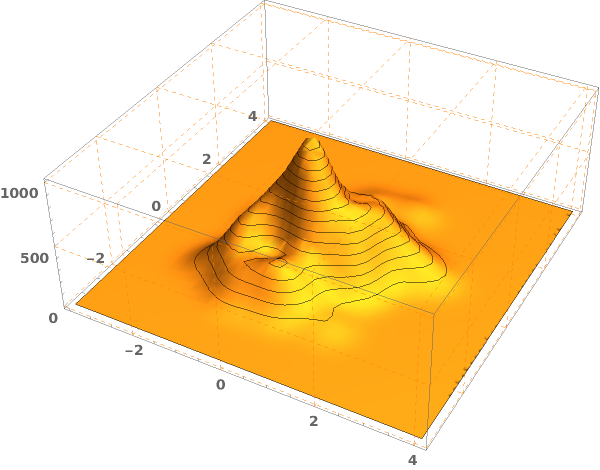
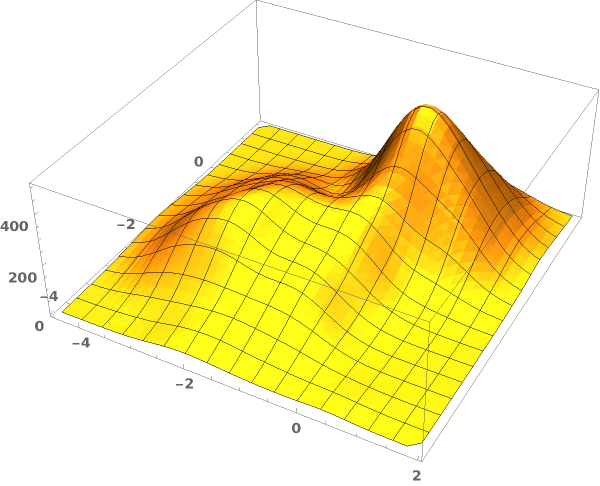
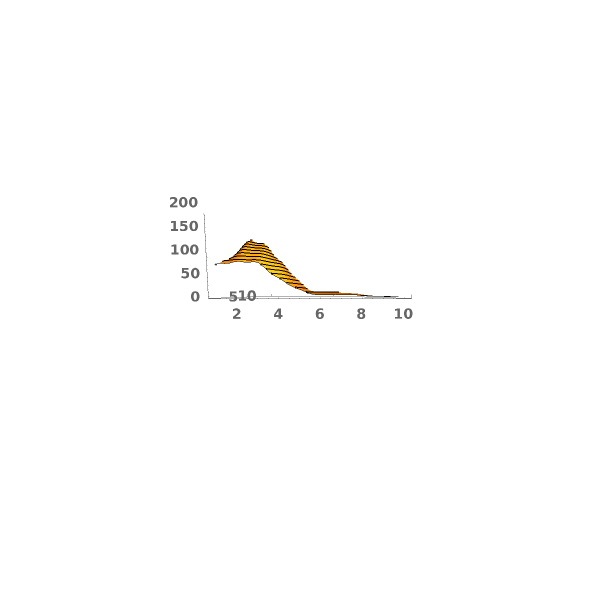
EmeraldSmoothHistogram3D[dataset]⟹chart
creates a SmoothHistogram3D from dataset.
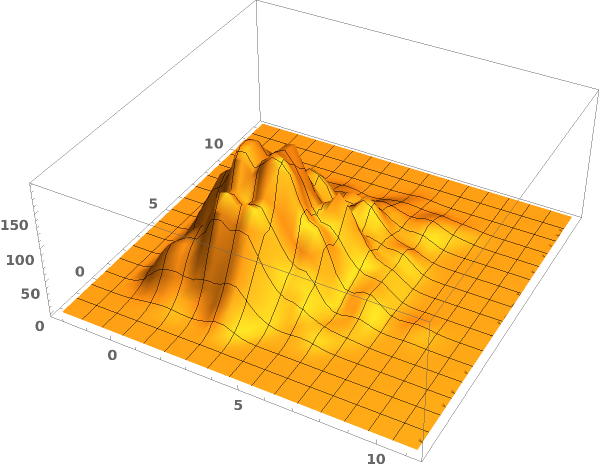
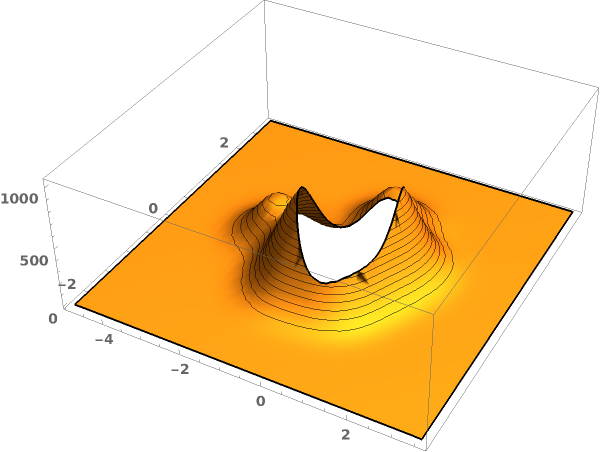
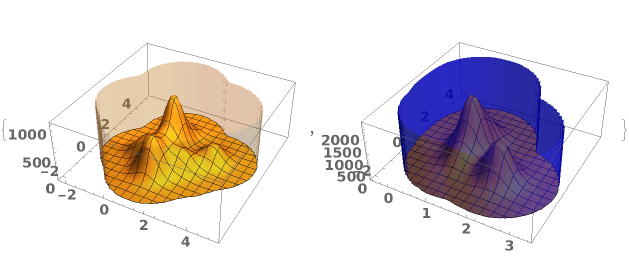
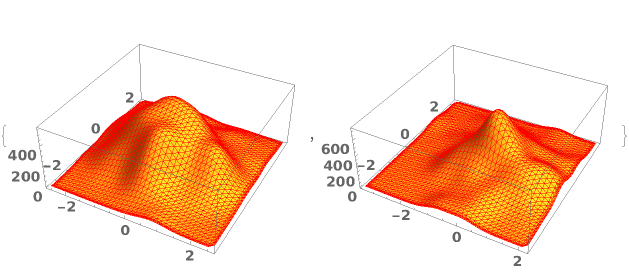
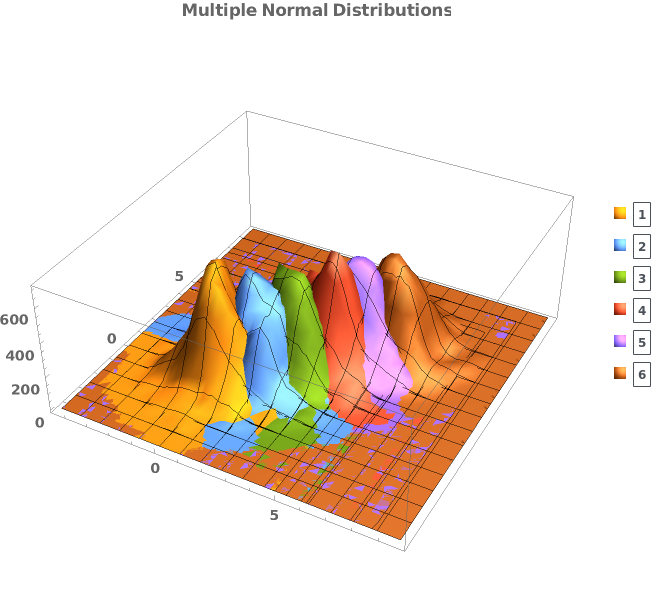
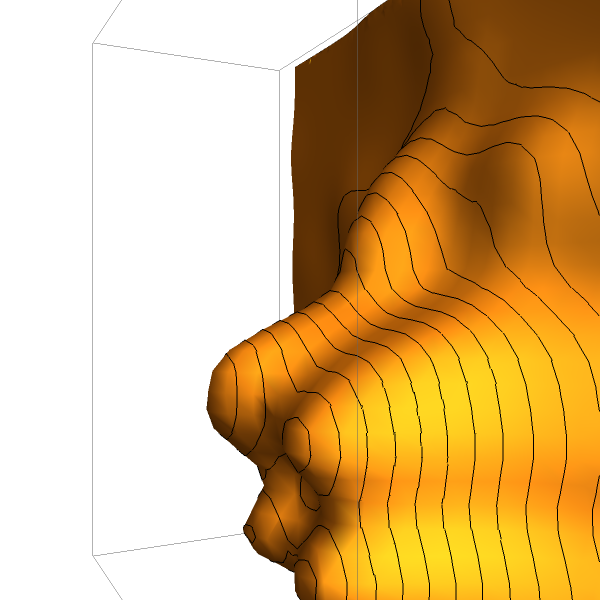
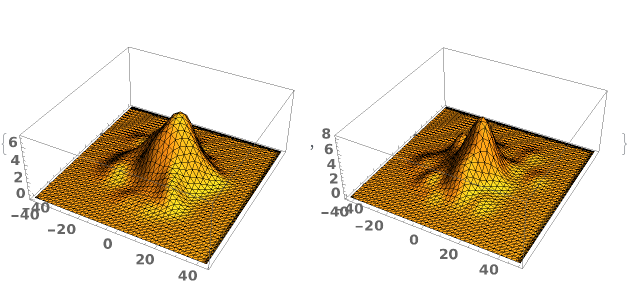
EmeraldSmoothHistogram3D[{datasets..}]⟹chart
creates a SmoothHistogram3D displaying each input dataset in datasets.
Details
Input
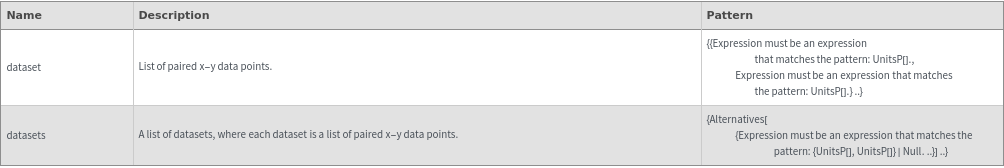
Output

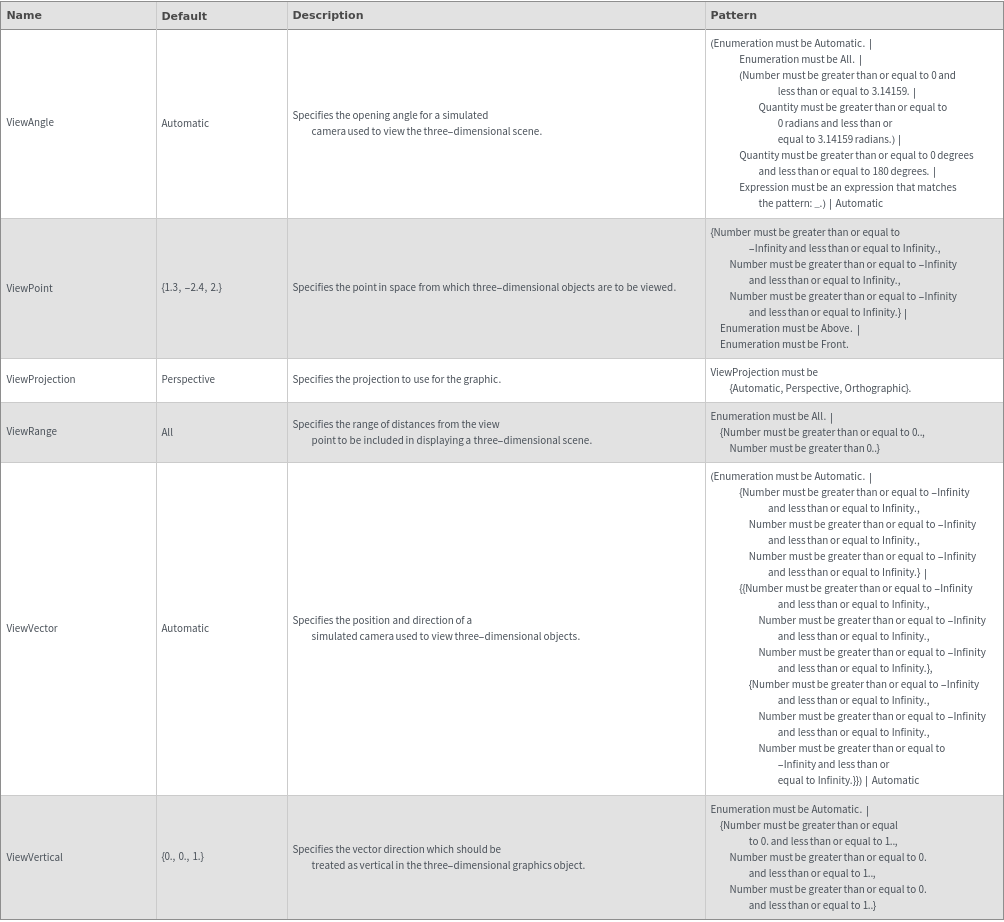
3D View Options
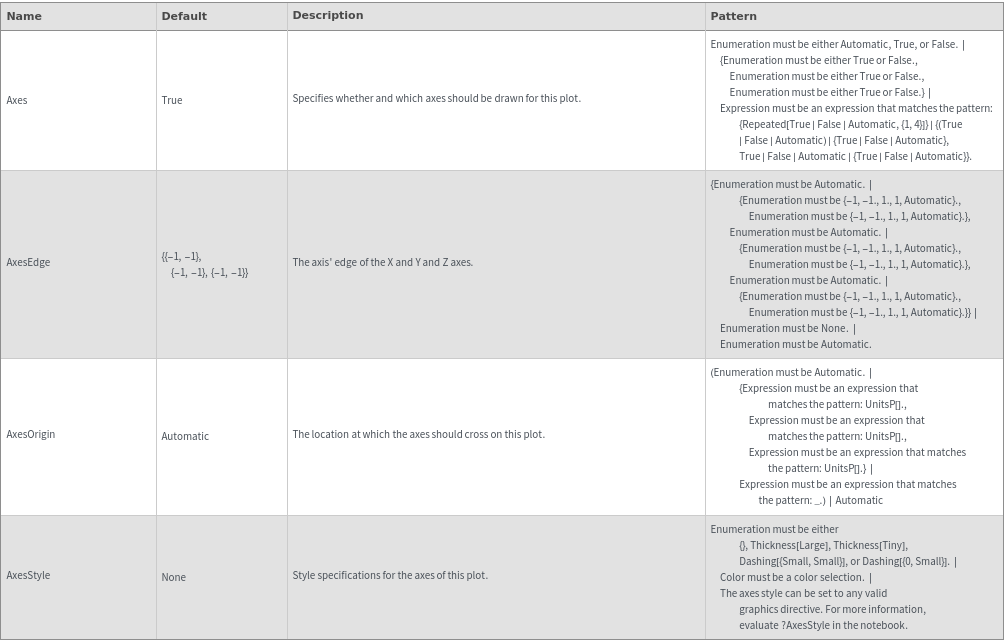
Axes Options
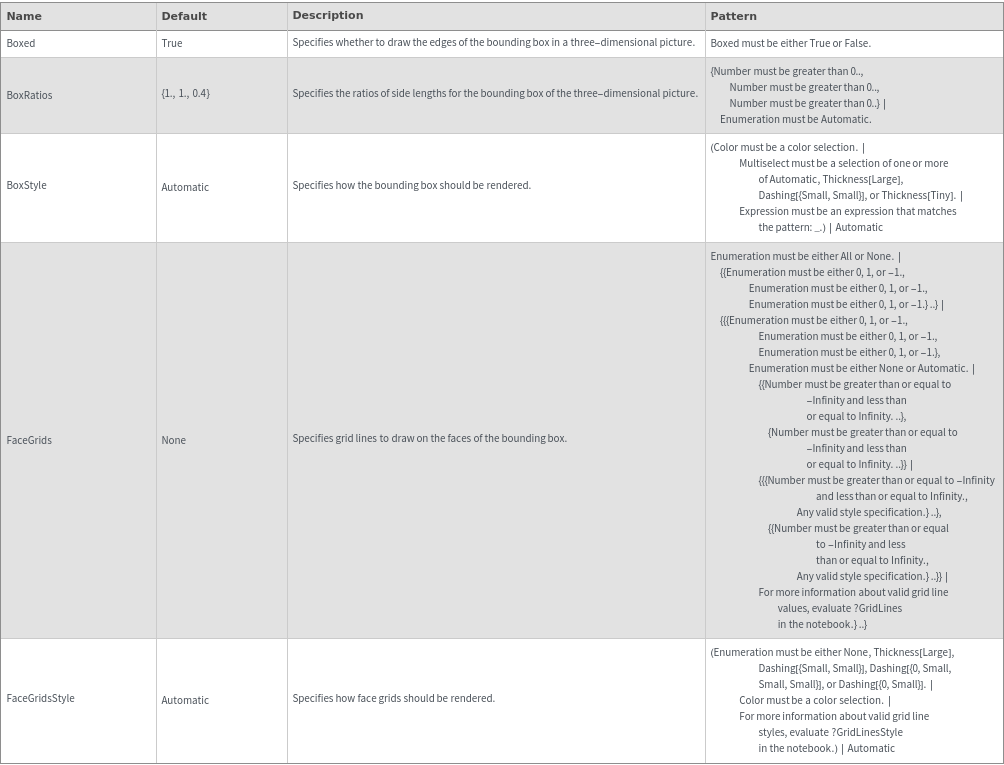
Box Options
Data Specifications Options

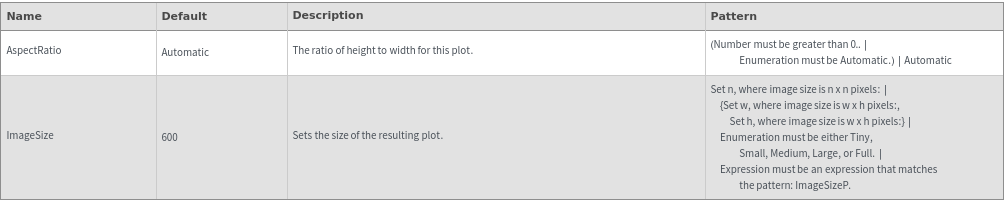
Image Format Options
Legend Options
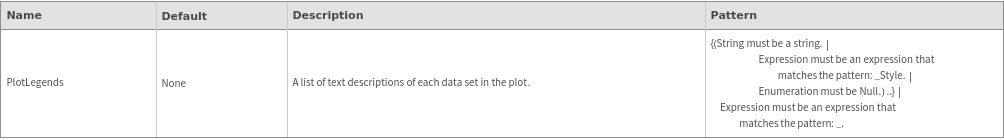
Mesh Options
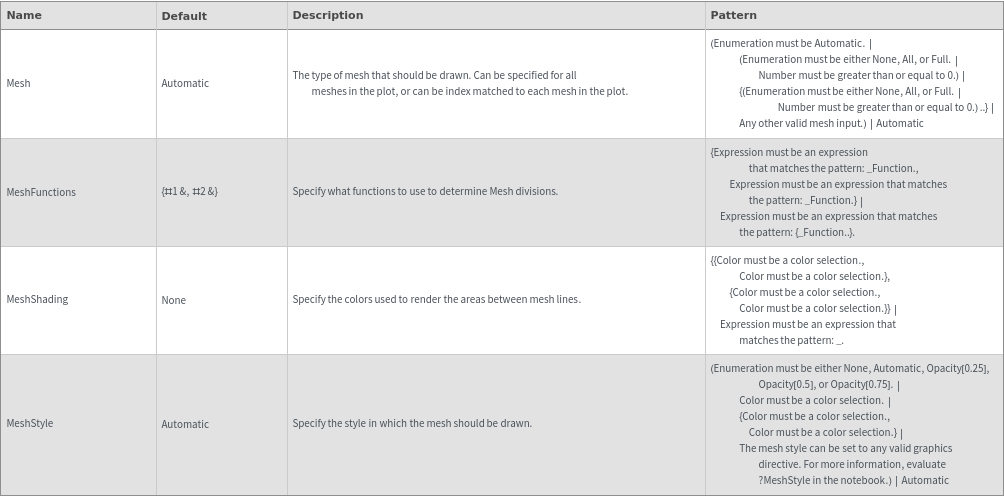
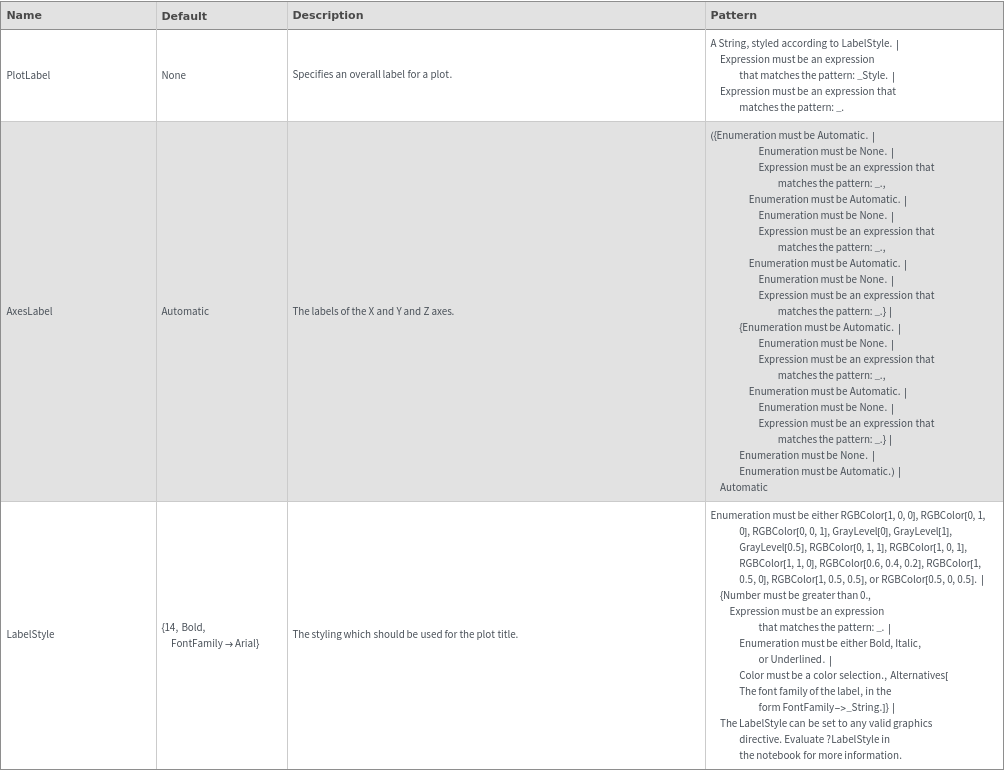
Plot Labeling Options
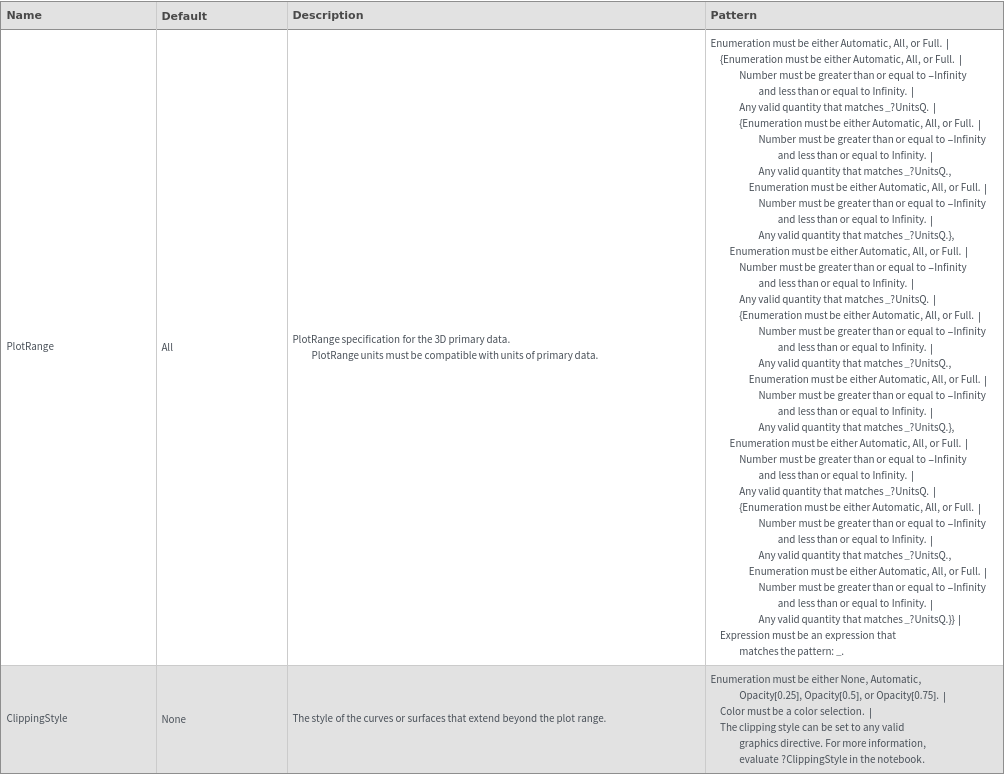
Plot Range Options
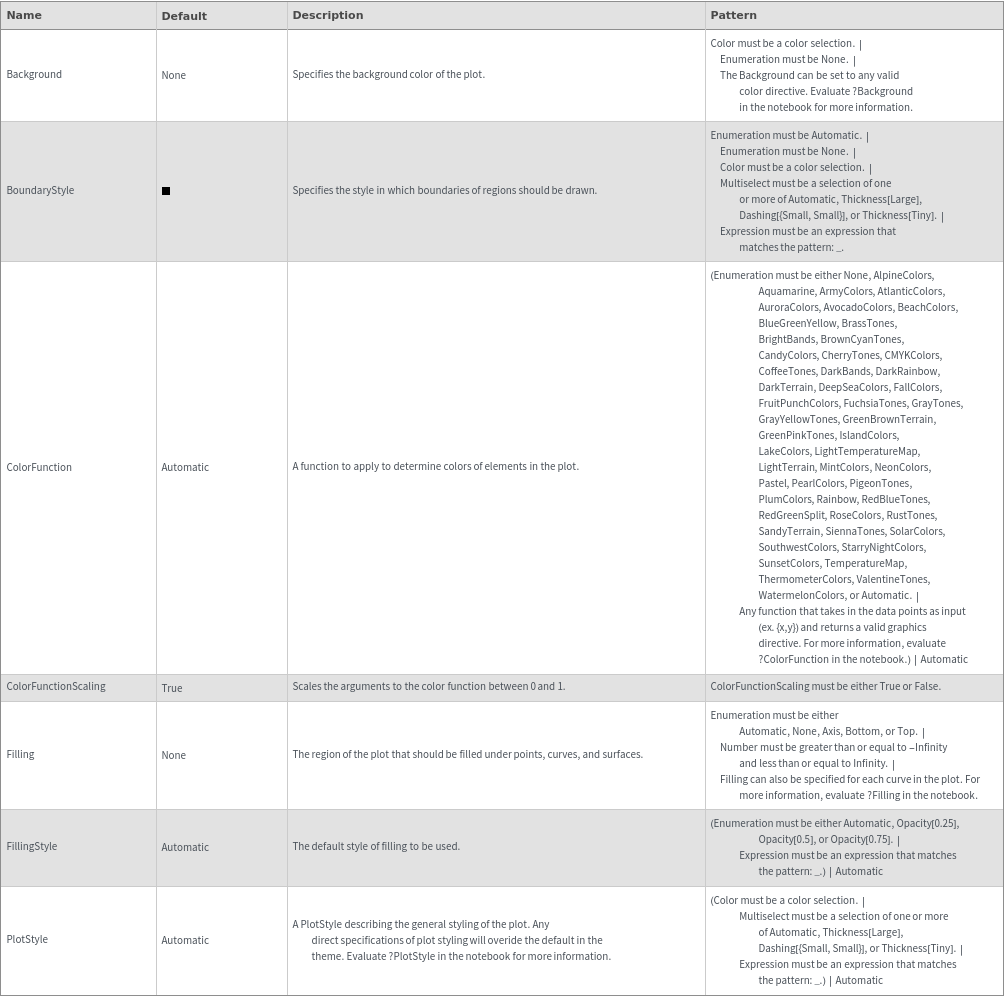
Plot Style Options
General Options