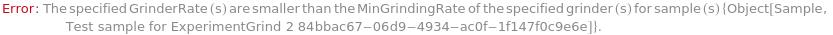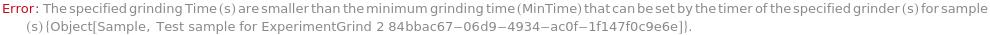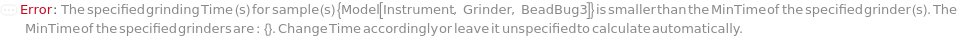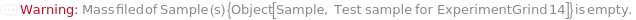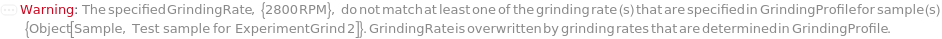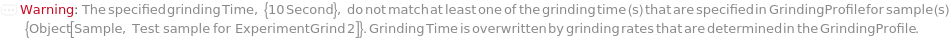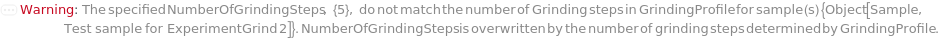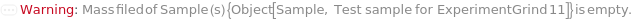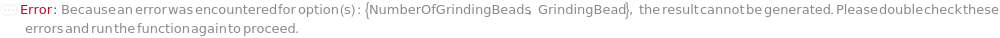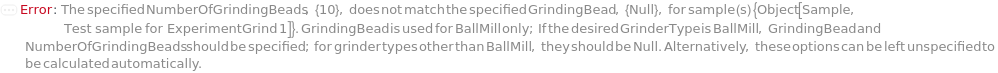ExperimentGrind
ExperimentGrind[Samples]⟹Protocol
generates a Protocol object to break particles of solid input Samples into smaller powder particles through mechanical actions.
ExperimentGrind is a method for reducing solid sample particles into finer powder using mechanical processes. ECL utilizes various grinder types, including ball mills, knife mills, and automated mortar grinders. Ball mills work by vibrating grinding containers filled with hard balls, where particle size reduction occurs through impact and friction between the balls and solid particles. Knife mills use rotating sharp blades to cut solid particles into smaller pieces, achieving size reduction through a cutting mechanism. Automated mortar grinders consist of a rotating bowl (mortar) and an angled revolving column (pestle), which apply pressure and friction to reduce particle size as the sample is ground between the mortar and pestle.
Experimental Principles
Figure 1.1: Procedural outline for ExperimentGrind: Step 1: Select a grinder. A grinder can be specified by Instrument option. ECL offers three grinder types, including BallMill, KnifeMill, and MortarGrinders, which can be specified by GrinderType option. Refer to Table 1 for detailed information about the grinders available at ECL. Step 2: Configure and perform grinding. Various grinding parameters can be specified, namely GrindingRate, Time, GrindingContainer, and NumberOfGrindingSteps. The NumberOfGrindingSteps option defines the number of grinding cycles, with CoolingTime intervals to prevent overheating. Refer to Table 1 for recommended grinding rates and times, and see the "Preferred Input Containers" section for information about compatible grinding containers. Step 3: Retrieve and store ground samples. Ground samples are transferred to containers specified by the ContainerOut option. SamplesOutStorageCondition option determines the storage conditions of the ground samples.
Instrumentation
BeadBug3
Figure 2.1: This diagram illustrates Beadbug3 grinder. It holds 3 * 2 mL non-skirted tubes. The grinding rate range is 2800 RPM to 4000 RPM and the grinding time is between 3 s and 3 min.
BeadGenie
Figure 2.2: This diagram illustrates Bead Genie grinder. It holds 12 * 1.5 or 2mL tubes, or 6 * 15mL tubes, or 3 * 50 mL tubes. The grinding rate range is 250 RPM to 2400 RPM and the grinding time is between 1 s and 99 min.
Mixer Mill MM400
Figure 2.3: This diagram illustrates Mixer Mill MM400. It can be used with grinding jars or grinding adapters of various sizes ranging from 0.2 mL to 50 mL. The grinding rate range is 180 RPM to 1800 RPM and the grinding time is between 10 s and 99 min.
Tube Mill Control
Figure 2.4: This diagram illustrates Tube Mill Control. Its grinding chamber holds up to 40 mL of the sample. The grinding rate range is 5000 RPM to 25000 RPM and the grinding time is between 5 s and 3 min.
Automated Mortar Grinder
Experiment Options
General
GrinderType
Method for reducing the size of the powder particles (grinding the sample into a fine powder). Options include BallMill, KnifeMill, and MortarGrinder. BallMill consists of a rotating or vibrating grinding container with sample and hard grinding balls inside in which the size reduction occurs through impact/friction of hard balls on/with the solid particles. KnifeMill consists of rotating sharp blades in which size reduction occurs through cutting of the solid particles into smaller pieces. Automated MortarGrinder consists of a rotating bowl (mortar) with the sample inside and an angled revolving column (pestle) in which size reduction occurs through pressure and friction between mortar, pestle, and sample particles.
Instrument
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Instrument, Grinder] or Object[Instrument, Grinder]
Programmatic Pattern: ObjectP[{Model[Instrument, Grinder], Object[Instrument, Grinder]}] | Automatic
Amount
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the minimum value for the specified grinder Instrument or All, whichever is less. If Instrument is not specified, Amount is automatically set to the minimum value of all grinders or All, which ever is less. Minimum value of a grinder is an estimated value which refers to the minimum of the sample that is ground efficiently by a specific grinder model.
Fineness
The approximate size of the largest particle in a solid sample. Fineness, Amount, and BulkDensity are used to determine a suitable grinder Instrument using PreferredGrinder function if Instrument is not specified.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 micrometer and less than or equal to 80 millimeters in increments of 1 micrometer.
BulkDensity
The mass of a volume unit of the powder. The volume for calculating BulkDensity includes the volumes of particles, internal pores, and inter-particle void spaces. This parameter is used to calculate the volume of a powder from its mass (Amount). The volume, in turn, is used along with the fineness in PreferredGrinder to determine a suitable grinder instrument if Instrument is not specified.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 milligram per milliliter and less than or equal to 25 grams per milliliter in increments of 1 milligram per milliliter.
Programmatic Pattern: RangeP[1*(Milligram/Milliliter), 25*(Gram/Milliliter), 1*(Milligram/Milliliter)]
GrindingContainer
The container that the sample is transferred into for the grinding process. Refer to the Instrumentation Table for more information about the containers that are used for each model of grinders.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to a suitable container based on the selected grinder Instrument and Amount of the sample.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Container, Vessel] or Model[Container, GrindingContainer]
Programmatic Pattern: ObjectP[{Model[Container, Vessel], Model[Container, GrindingContainer]}] | Automatic
GrindingBead
In ball mills, grinding beads or grinding balls are used along with the sample inside the grinding container to beat and crush the sample into fine particles as a result of rapid mechanical movements of the grinding container.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Item, GrindingBead] or Object[Item, GrindingBead] or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (ObjectP[{Model[Item, GrindingBead], Object[Item, GrindingBead]}] | Automatic) | Null
NumberOfGrindingBeads
In ball mills, determines how many grinding beads or grinding balls are used along with the sample inside the grinding container to beat and crush the sample into fine particles.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to a number of grinding beads that roughly have the same volume as the sample if GrinderType is set to BallMill. The number is estimated based on the estimated volume of the sample and diameter of the selected GrindingBead, considering 50% of packing void volume. When calculated automatically, NumberOfGrindingBeads will not be less than 1 or greater than 20.
GrindingRate
Indicates the speed of the circular motion exerted by grinders to pulverize the samples into smaller powder particles.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the default RPM for the selected grinder Instrument according to the values in the Instrumentation Table.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0.01 hertz and less than or equal to 420 hertz or greater than or equal to 1 revolution per minute and less than or equal to 25000 revolutions per minute.
Time
Default Calculation: Automatically set to a default value based on the Instrument selection according to Instrumentation Table.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 second and less than or equal to 72 hours in increments of 1 second.
Duty Cycle
NumberOfGrindingSteps
Determines how many times the grinding process is interrupted for cool down to completely grind the sample and prevent excessive heating of the sample. Between each grinding step there is a cooling time that the grinder is switched off to cool down the sample and prevent excessive rise in sample's temperature.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to 1 or determined based on the specified GrindingProfile Option.
CoolingTime
Determines the duration of time between each grinding step that the grinder is switched off to cool down the sample and prevent excessive rise in the sample's temperature.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 second and less than or equal to 72 hours in increments of 1 second or Null.
GrindingProfile
A set of steps of the grinding process, with each step provided as {grinding rate, grinding time} or as {wait time} indicating a cooling period to prevent the sample from overheating.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to reflect the selections of GrindingRate, Time, NumberOfGrindingSteps, and CoolingTime.
Programmatic Pattern: {({RangeP[0*RPM, 25000*RPM] | RangeP[0*Hertz, 420*Hertz], RangeP[1*Second, $MaxExperimentTime, 1*Second]} | {RangeP[1*Second, $MaxExperimentTime, 1*Second]})..} | Automatic
Storage Information
ContainerOut
Default Calculation: Automatically set to a preferred container based on the result of PreferredContainer function. PreferredContainer function returns the smallest model of ECL standardized container which is compatible with model and can hold the provided volume.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Container, Vessel] or Object[Container, Vessel] or a prepared sample.
Programmatic Pattern: (ObjectP[{Model[Container, Vessel], Object[Container, Vessel]}] | _String) | Automatic
SamplesOutStorageCondition
The non-default conditions under which any new samples generated by this experiment should be stored after the protocol is completed. If left unset, the new samples will be stored according to their StorageCondition or their Models' DefaultStorageCondition.
Pattern Description: {AmbientStorage, EnclosedAmbientStorage, Refrigerator, Freezer, DeepFreezer, CryogenicStorage, YeastIncubation, YeastShakingIncubation, BacterialIncubation, BacterialShakingIncubation, MammalianIncubation, ViralIncubation, CrystalIncubation, AcceleratedTesting, IntermediateTesting, LongTermTesting, UVVisLightTesting}, Desiccated, VacuumDesiccated, RefrigeratorDesiccated, or Disposal or an object of type or subtype Model[StorageCondition] or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((SampleStorageTypeP | Desiccated | VacuumDesiccated | RefrigeratorDesiccated | Disposal) | ObjectP[Model[StorageCondition]]) | Null
Model Input
PreparedModelContainer
Indicates the container in which a Model[Sample] specified as input to the experiment function will be prepared.
Default Calculation: If PreparedModelAmount is set to All and when the input model has a product associated with both Amount and DefaultContainerModel populated, automatically set to the DefaultContainerModel value in the product. Otherwise set to Model[Container, Vessel, "2mL Tube"].
PreparedModelAmount
Indicates the amount of a Model[Sample] specified as input to the experiment function that will be prepared in the PreparedModelContainer. When set to All and the input model sample is not preparable, the entire amount of the input model sample that comes from one of the Products is prepared. The selected product must have both Amount and DefaultContainerModel populated, and it must not be a KitProduct. When set to All and the input model is preparable such as water, 1 Milliliter of the input model sample is prepared.
Sample Prep Options
Sample Preparation
PreparatoryUnitOperations
Specifies a sequence of transferring, aliquoting, consolidating, or mixing of new or existing samples before the main experiment. These prepared samples can be used in the main experiment by referencing their defined name. For more information, please reference the documentation for ExperimentSamplePreparation.
Protocol Options
Organizational Information
Template
A template protocol whose methodology should be reproduced in running this experiment. Option values will be inherited from the template protocol, but can be individually overridden by directly specifying values for those options to this Experiment function.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Object[Protocol] or an object of type or subtype of Object[Protocol] with UnresolvedOptions, ResolvedOptions specified or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (ObjectP[Object[Protocol]] | FieldReferenceP[Object[Protocol], {UnresolvedOptions, ResolvedOptions}]) | Null
Name
A object name which should be used to refer to the output object in lieu of an automatically generated ID number.
Post Experiment
MeasureWeight
Indicates if any solid samples that are modified in the course of the experiment should have their weights measured and updated after running the experiment. Please note that public samples are weighed regardless of the value of this option.
MeasureVolume
Indicates if any liquid samples that are modified in the course of the experiment should have their volumes measured and updated after running the experiment. Please note that public samples are volume measured regardless of the value of this option.
ImageSample
Example Results
ExperimentGrind[
Model[Sample,"Coarse Grain Pink Salt (Sodium Chloride)"],
PreparedModelAmount -> 1 Gram,
PreparedModelContainer -> Model[Container, Vessel, "2mL Tube"],
Instrument -> Model[Instrument, Grinder, "Automated Mortar Grinder"],
GrindingRate -> 70 RPM,
Time -> 1 Hour,
NumberOfGrindingSteps -> 1
]
ExperimentGrind[
Object[Sample,"Coarse salt for ExperimentGrind help files"],
Instrument -> Model[Instrument, Grinder, "Automated Mortar Grinder"],
GrindingRate -> 70 RPM,
Time -> 1 Hour,
NumberOfGrindingSteps -> 1
]
Object[Protocol,Grind,"id:1ZA60vzeGYl5"]
Example Calls
Preferred Input Containers
Model[Instrument, Grinder, "BeadBug3" is compatible only with skirtless 2 mL conical tubes. Optimal sample amount for this container is approximately 0.2 - 1 mL
Model[Instrument, Grinder, "BeadGenie" is compatible with 1.5, 2, 15, and 50 mL conical tubes. It holds 12 microtubes (1.5/2 mL), 6 15 mL, or 3 50 mL conical tubes. Optimal sample amount for these containers are approximately 0.2-1 mL, 1-7.5mL, and 7.5-20mL, respectively.
Model[Instrument, Grinder, "Mixer Mill MM400"] is compatible with a range of grinding jars and tubes in various volumes. Currently, only the listed containers are available at ECL. Additional containers or adapters can be acquired upon request. Optimal sample amount for these containers are approximately 7.5 - 20 mL.
Warnings and Errors
Messages (31)
CoolingTimeMismatch (1)
GrinderTypeOptionMismatch (1)
GrindingBeadMismatch (2)
HighGrindingRate (2)
HighGrindingTime (2)
InsufficientAmount (1)
InvalidSamplesOutStorageCondition (1)
LargeParticles (1)
LowGrindingRate (2)
LowGrindingTime (2)
ModifiedCoolingTimes (1)
ModifiedGrindingRates (1)
ModifiedGrindingTimes (1)
ModifiedNumberOfGrindingSteps (1)
NumberOfGrindingBeadsMismatch (2)
ObjectDoesNotExist (6)
Do NOT throw a message if we have a simulated container but a simulation is specified that indicates that it is simulated:
Do NOT throw a message if we have a simulated sample but a simulation is specified that indicates that it is simulated:
Throw a message if we have a container that does not exist (ID form):
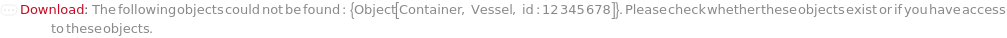
Throw a message if we have a container that does not exist (name form):
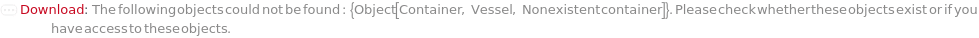
Throw a message if we have a sample that does not exist (ID form):
Throw a message if we have a sample that does not exist (name form):
Last modified on Wed 8 Oct 2025 13:11:20