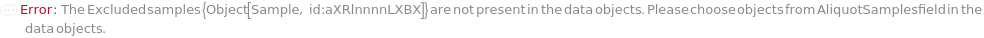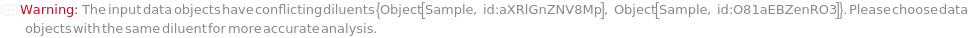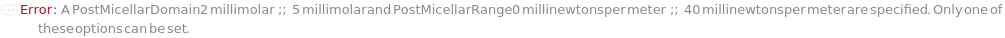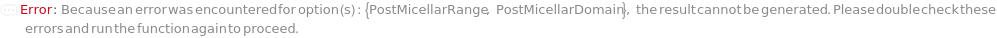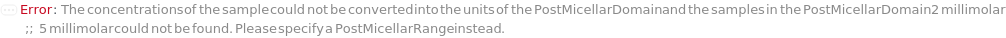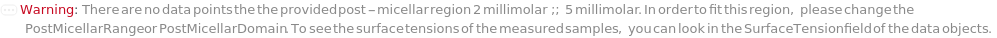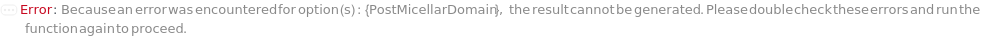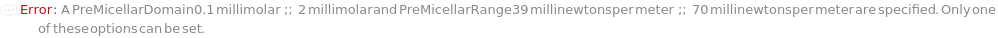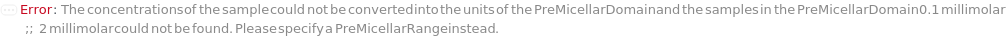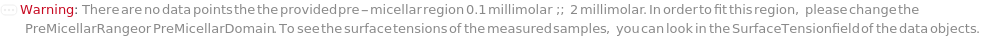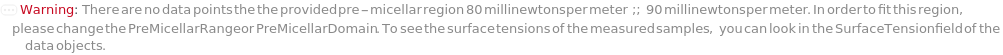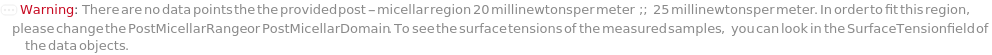AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration
AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration[data]⟹object
calculates the CriticalMicelleConcentration of the TargetMolecule in the samples of the provided SurfaceTension data. The input data is generated by ExperimentMeasureSurfaceTension.
AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration[protocol]⟹object
calculates the CriticalMicelleConcentration of the TargetMolecule in the samples of the provided MeasureSurfaceTension protocol. The input data is generated by ExperimentMeasureSurfaceTension.
Details
- The CriticalMicelleConcentration of a TargetMolecule is calculated using the SurfaceTension values of all of the AliquotSamples.
- Surface tension is defined as the work required to expand a surface by an area. The accumulation of surface active compounds at the air-water interface lowers the surface tension. This can be described by the Gibbs adsorption isotherm detailed in Object[Report, Literature, "id:n0k9mG8wBBXr"]. A plot of surface tension vs. Ln[concentration] can be used to determine the Critical Micelle Concentration, Apparent Partitioning Coefficient, Surface Excess Concentration and Cross Sectional Area of the surfactant. The Critical Micelle Concentration is the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form and all additional surfactants added to the system go to micelles. This is determined with the intersection of linear fits of points in the premicellar region and postmicellar region. The Apparent Partitioning Coefficient is the inverse of the concentration where increasing the concentration of the sample starts decreasing the surface tension. This is determined with the intersection of premicellar region fit and the surface tension of the diluent. The Surface Excess Concentration is the amount of surfactant adsorbed at the air water interface per surface area, calculated by taking the negative of the slope premicellar region fit divided by the temperature and ideal gas constant. The Cross Sectional Area is calculated by taking the inverse of the SurfaceExcessConcentration and the Avogadro constant.
Input

Output

General Options

Method Options
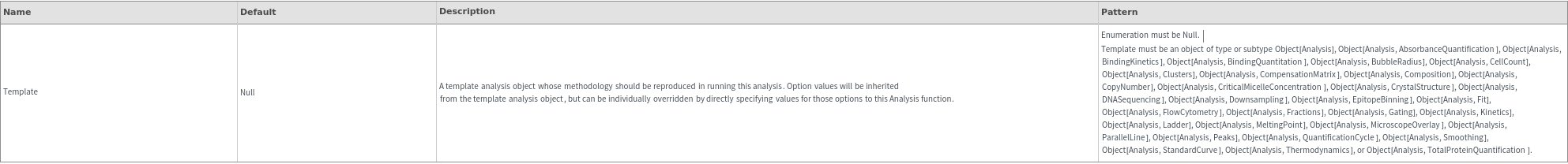
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (4)
Given an Object[Protocol,MeasureSurfaceTension], AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration returns an Analysis Object:
Given an Object[Data,SurfaceTension], AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration returns an Analysis Object:
AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration populates the PreMicellarFit, PostMicellarFit, CriticalMicelleConcentration, ApparentPartitioningCoefficient, SurfaceExcessConcentration, CrossSectionalArea, MaxSurfacePressure fields:
AnalyzeCriticalMicelleConcentration populates the TargetMolecules, Concentrations, SurfaceTensions, Temperatures, SurfacePressures fields:
Additional Examples (2)
Options (17)
DiluentSurfaceTension (3)
PostMicellarDomain (2)
PostMicellarRange (2)
PreMicellarDomain (2)
PreMicellarRange (2)
TargetMolecules (3)
Messages (13)
Give an error stating that the samples to be excluded from the fit are not present in the data: