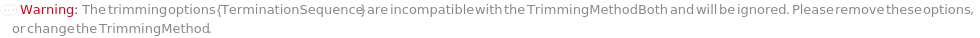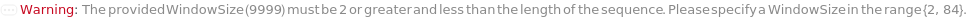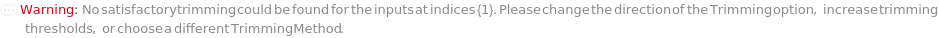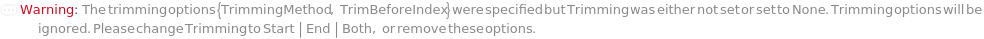AnalyzeDNASequencing
AnalyzeDNASequencing[sequencingData]⟹sequence
conducts base-calling analysis to assign a DNA sequence to the electropherogram peaks in sequencingData.
AnalyzeDNASequencing[sequencingProtocol]⟹sequences
conducts base-calling analysis to assign DNA sequences to all sequencing data present in sequencingProtocol.
AnalyzeDNASequencing[xyData]⟹sequence
conducts base-calling analysis to assign a DNA sequence to the raw electropherogram traces represented by xyData.
Details
- The Phred Method is an implementation of the base-calling algorithm of Ewing et al. described in Object[Report, Literature, "id:N80DNj1P84VX"]: B. Ewing et al. "Base-Calling of Automated Sequencer Traces using Phred." Genome Research 8.3 (1998): 175-185.
- The Phred quality score Q = -10 Log10[P], where P is the probability of incorrect assignment. For example, 99% accuracy is equivalent to P = 0.01, or a quality score of Q = 20.
- A quality value of >20 is considered an accurate assignment, quality between 15-19 is considered mediocre accuracy, and a quality value below 15 is considered poor accuracy.
Input

Output

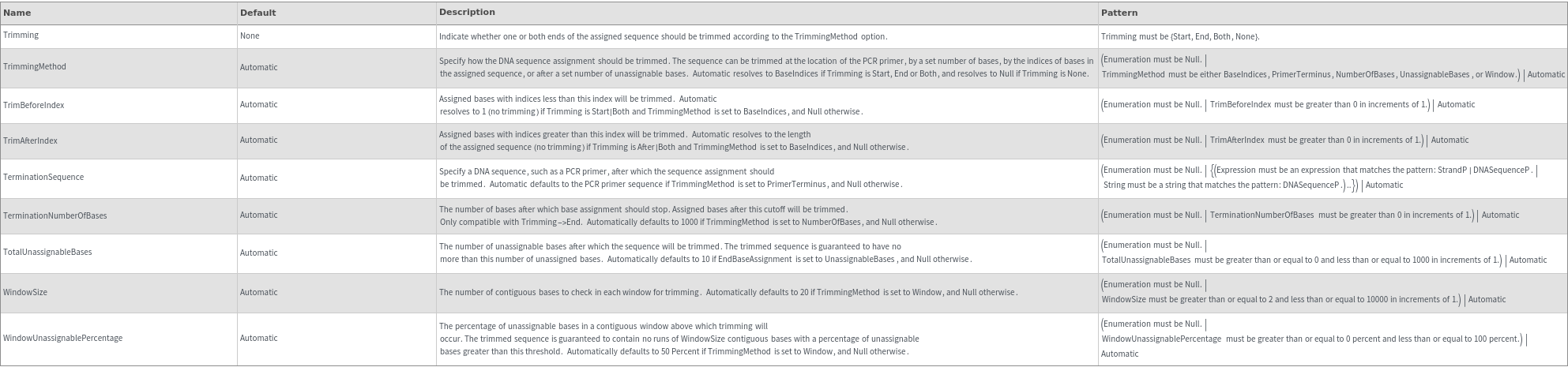
Assignment Options

Trimming Options
Method Options
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Additional Examples (4)
Input Types (3)
Conduct sequence analysis on raw electropherograms. Electropherograms must have the same cycle reads (x-axis values), and must be supplied in {A,C,G,T} order:
Conduct sequence analysis on a list of DNASequencing data objects:
Conduct sequence analysis on all data objects in all protocols in a list of protocols:
Options (25)
Method (1)
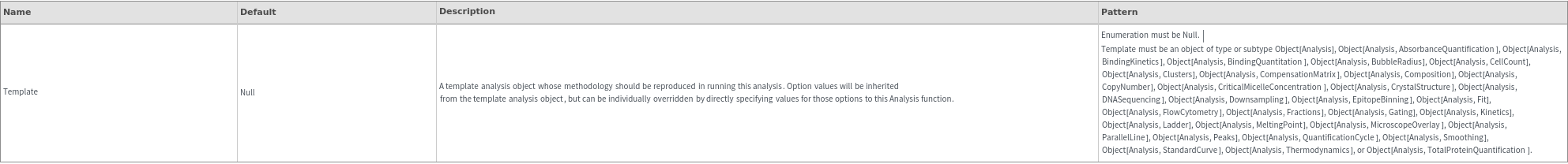
Template (1)
TerminationNumberOfBases (2)
TerminationSequence (3)
When Trimming is set to Start or End, trimming will start from the requested direction and stop upon detecting the first occurence of one of the sequences in TerminationSequence:
The sequence will also be checked for any occurences of the reverse complements of sequences in TermationSequence:
When trimming is set to Both, the longest contiguous subsequence between termination sequences (or the sequence ends) will be returned:
TotalUnassignableBases (2)
Trimming (4)
TrimmingMethod (5)
Trim sequence where subsequences (or their reverse complements) in TerminationSequence are identified in the called sequence. See option TerminationSequence for more information:
Trim sequence by base indices, trimming all bases before the 10th base and after the 60th base:
Trim sequence after a set number of bases. This trimming method is only compatible with Trimming->End:
Trim until the trimmed sequence has a total unassingable base count lower than a set threshold:
Trim such that the trimmed sequence contains no windows of 3 contiguous bases in which more than 50 Percent of the bases cannot be assigned ("N"):