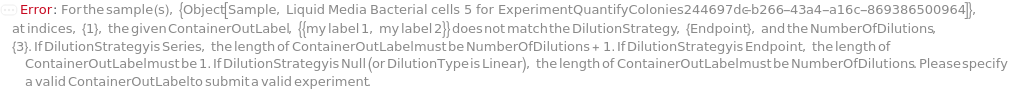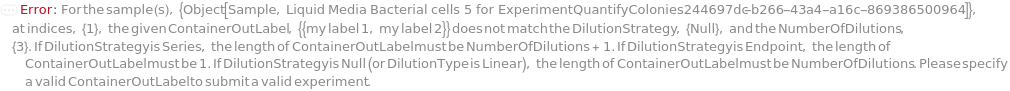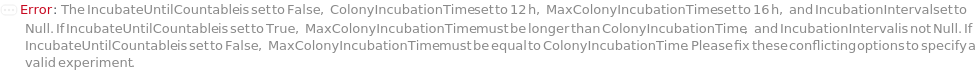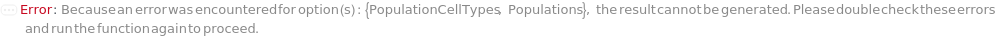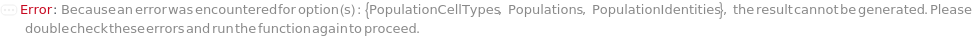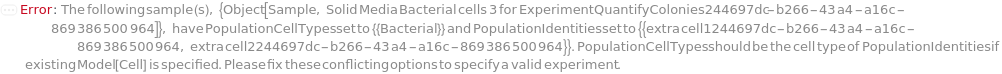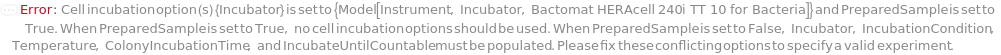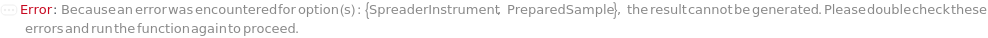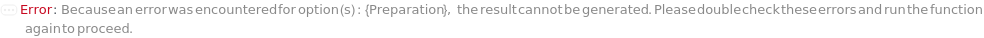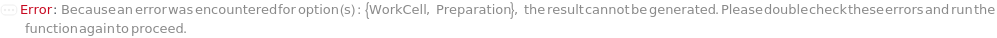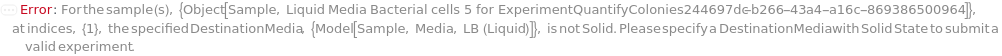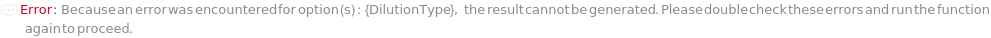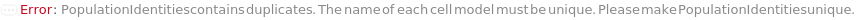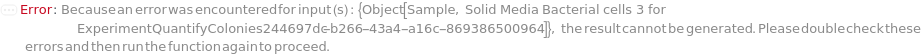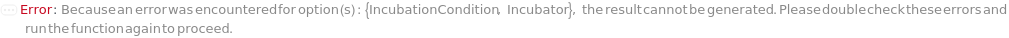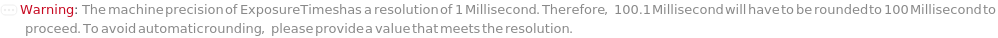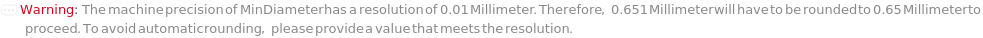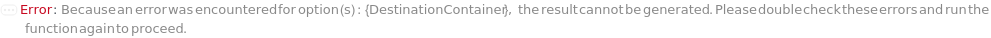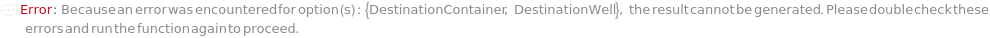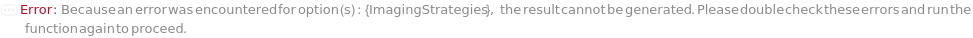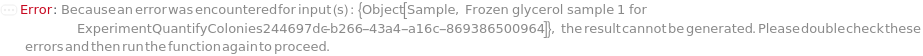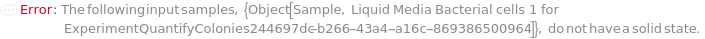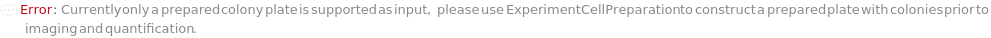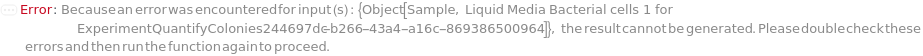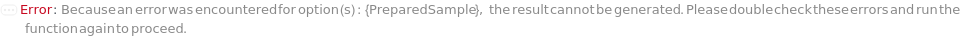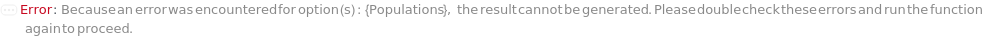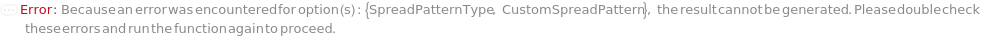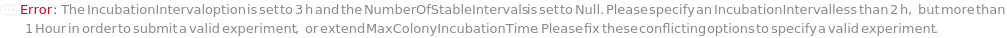General
ImagingInstrument
The instrument used to image colonies on solid media.
Default Value: Model[Instrument, ColonyHandler, QPix 420 HT]
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Instrument, ColonyHandler] or Object[Instrument, ColonyHandler]
Programmatic Pattern: ObjectP[{Model[Instrument, ColonyHandler], Object[Instrument, ColonyHandler]}]
PreparedSample
Indicates if the provided samples containing microbial cells that are counted have been previously transferred onto a solid media plate and cultivated to grow colonies. If PreparedSample is set to True, the provided sample container is placed directly into the imaging instrument for imaging and counting, bypassing the cell spreading and incubation steps.
Default Calculation: Set to False if the provided samples is not in the state of Solid, otherwise set to True.
Pattern Description: True or False.
Programmatic Pattern: BooleanP | Automatic
SpreaderInstrument
The colony handler that is used to spread the provided samples on solid media to prepare colony samples.
Default Calculation: When PreparedSample is set to False, automatically set SpreaderInstrument to Model[Instrument, ColonyHandler, "QPix 420 HT"].
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Instrument, ColonyHandler] or Object[Instrument, ColonyHandler] or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (ObjectP[{Model[Instrument, ColonyHandler], Object[Instrument, ColonyHandler]}] | Automatic) | Null
Incubator
The cell incubator that is used to grow colonies in the desired environment before colonies are imaged. Custom incubation actively selects an incubator in the lab and uses a thread to incubate only the cells from this protocol for the specified Time. Selecting a default IncubationCondition (BacterialIncubation, YeastIncubation) will passively store the cells for the specified time in a shared incubator, potentially with samples from other protocols. However, it will not consume a thread while the cells are inside the incubator.
Default Calculation: When PreparedSample is set to False, automatically set Incubator to an incubator that meets the requirements according to IncubateCellsDevices that provides desired incubation conditions.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Instrument, Incubator] or Object[Instrument, Incubator] or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (ObjectP[{Model[Instrument, Incubator], Object[Instrument, Incubator]}] | Automatic) | Null
WorkCell
Indicates the work cell that this primitive will be run on if Preparation->Robotic.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to qPix if Preparation->Robotic.
Pattern Description: QPix or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (qPix | Automatic) | Null
Preparation
Indicates if this unit operation is carried out primarily robotically or manually. Manual unit operations are executed by a laboratory operator and robotic unit operations are executed by a liquid handling work cell.
Pattern Description: Manual or Robotic.
Programmatic Pattern: PreparationMethodP | Automatic
Imaging
ImagingStrategies
The end goals for capturing images. ImagingStrategies can be either a single end goal of simple visualization or a list of multiple end goals. The options include BrightField, BlueWhiteScreen, and various fluorescence imaging techniques. BrightField imaging provides essential baseline images and is required if any other imaging strategies are employed. BlueWhiteScreen is used to distinguish recombinant colonies with disrupted lacZ (white colonies) from blue colonies, using an absorbance filter. Fluorescence imaging allows for the visualization of colonies with fluorescent dyes or proteins.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to include BlueWhiteScreen along with BrightField if Populations is set to include BlueWhiteScreen; set to include a specific fluorescence strategy along with BrightField if the Model[Cell] information in the sample matches one of the fluorescent excitation and emission pairs supported by the imaging instrument. Otherwise, set to BrightField, as a BrightField image is always taken.
Pattern Description: Multiple Imaging Strategies or Single Imaging Strategy.
Programmatic Pattern: (DuplicateFreeListableP[BrightField | BlueWhiteScreen | VioletFluorescence | GreenFluorescence | OrangeFluorescence | RedFluorescence | DarkRedFluorescence] | BrightField) | Automatic
Index Matches to: experiment samples
ExposureTimes
A single length of time that the camera sensor collects light during image acquisition for each imaging strategy. An increased exposure time leads to brighter images based on a linear scale. When set as Automatic, optimal exposure time is automatically determined during the experiment. This is done by running AnalyzeImageExposure on images taken with suggested initial exposure times. The process adjusts the exposure time for subsequent image acquisitions until the optimal value is found.
Pattern Description: Multiple Exposure Times or Single Exposure Time.
Programmatic Pattern: ({(RangeP[1*Millisecond, 2000*Millisecond] | Automatic)..} | (RangeP[1*Millisecond, 2000*Millisecond] | Automatic)) | Automatic
Index Matches to: experiment samples
Spreading
DilutionType
Indicates the type of dilution performed on the sample. Linear dilution represents a single stage dilution of the Analyte in the sample to a specified concentration or by a specified dilution factor. Serial dilution represents a stepwise dilution of the Analyte in the sample resulting in multiple samples and a geometric progression of the concentration. The progression can be described by either a series of target concentrations or a series of dilution factors. In a serial dilution the source of a dilution round is the resulting sample of the previous dilution round. The first source sample is the original sample provided.
Pattern Description: Serial or Linear or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Null | DilutionTypeP) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
DilutionStrategy
Indicates if only the final sample (Endpoint) or all diluted samples (Series) produced by serial dilution are used for spreading on solid media plate.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to Endpoint if Dilute is True and DilutionType is Serial.
Pattern Description: Series or Endpoint or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Null | DilutionStrategyP) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
NumberOfDilutions
For each sample, the number of diluted samples to prepare.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the length of TargetAnalyteConcentration, CumulativeDilutionFactor, or SerialDilutionFactor if provided, otherwise set to 1.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 100 in increments of 1 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Null | RangeP[1, $MaxNumberOfDilutions, 1]) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
CumulativeDilutionFactor
For each sample, the factor by which the concentration of the TargetAnalyte in the original sample is reduced during the dilution. The length of this list must match the corresponding value in NumberOfDilutions.
Default Calculation: Automatically set based on the systems of equations specified under the DilutionType option.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 100000000000000000000000 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Null | RangeP[1, 10^23]) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
Nested Index Matches to: experiment samples
SerialDilutionFactor
For each sample, the factor by which the concentration of the TargetAnalyte in the resulting sample of the previous dilution step is reduced. For example, if the CumulativeDilutionFactor is equal to {10,100,1000}. SerialDilutionFactor will resolve to {10,10,10}. The length of this list must match the corresponding value in NumberOfDilutions.
Default Calculation: Automatically set based on the systems of equations specified under the DilutionType option.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 100000000000000000000000 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Null | RangeP[1, 10^23]) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
Nested Index Matches to: experiment samples
ColonySpreadingTool
For each sample, the tool used to spread the suspended cells from the input sample onto the destination plate or into a destination well.
Default Calculation: If DestinationContainer is an 8 well solid media tray, resolves to Model[Part, ColonyHandlerHeadCassette, "8-pin spreading head"]. Otherwise resolves to Model[Part, ColonyHandlerHeadCassette, "1-pin spreading head"].
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Part, ColonyHandlerHeadCassette] or Object[Part, ColonyHandlerHeadCassette] or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (ObjectP[{Model[Part, ColonyHandlerHeadCassette], Object[Part, ColonyHandlerHeadCassette]}] | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
SpreadVolume
For each sample, the volume of suspended cells to transfer to the agar gel to be spread.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the median among 30 Microliter, the sample volume divided by the length of dispense coordinates, and 100 Microliter.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 10 microliters and less than or equal to 130 microliters or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (RangeP[10*Microliter, 130*Microliter] | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
DispenseCoordinates
For each sample, the location to dispense the suspended cells to be spread on the destination plate.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the first coordinate of the resolved SpreadPattern.
Pattern Description: List of one or more {XCoordinate, YCoordinate} entries or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ({{RangeP[-63*Millimeter, 63*Millimeter], RangeP[-43*Millimeter, 43*Millimeter]}..} | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
SpreadPatternType
For each sample, the pattern the spreading colony handler head will move when spreading the colony on the plate. Can be specified as a pre-determined pattern or Custom to indicate the coordinates in CustomSpreadPattern should be used.
Default Calculation: If PreparedSample is set to False, automatically set to Spiral.
Pattern Description: Spiral, VerticalZigZag, HorizontalZigZag, or Custom or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (SpreadPatternP | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
CustomSpreadPattern
For each sample, the user defined pattern used to spread the suspended cells across the plate. Specify a series of Spread[{{xCoordinate,yCoordinate}}..] to specify the pattern. In order to draw separate lines, specify series of coordinates in different Spread[...]'s. Between each Spread[...], the pin on colony spreading tool will be lifted off of the agar and then repositioned at the first coordinate of the next Spread[...].
Pattern Description: Multiple Spread strokes or Single Spread stroke or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Null | (Verbatim[Spread][{{RangeP[-63*Millimeter, 63*Millimeter], RangeP[-43*Millimeter, 43*Millimeter]}..}] | {Verbatim[Spread][{{RangeP[-63*Millimeter, 63*Millimeter], RangeP[-43*Millimeter, 43*Millimeter]}..}]..})) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
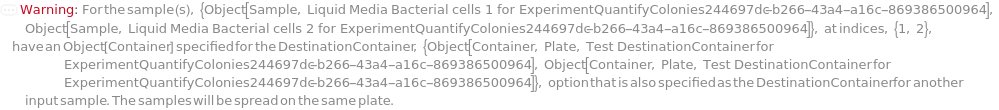
DestinationContainer
For each Sample, the desired type of container to have suspended cells spread in, with indices indicating grouping of samples in the same plate, if desired.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Model[Container] or Object[Container] or a prepared sample or {Index, Container} or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (((ObjectP[{Model[Container], Object[Container]}] | _String) | {GreaterEqualP[1, 1] | Automatic, (ObjectP[{Model[Container]}] | _String) | Automatic}) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
DestinationWell
For each Sample, the well of the DestinationContainer to spread the suspended cells.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to A1.
Pattern Description: Any well from A1 to P24 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (WellPositionP | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
DestinationMedia
For each sample, the media on which the cells are spread.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the PreferredSolidMedia field of the first Model[Cell] of the composition of the Sample.
Pattern Description: An object of type or subtype Object[Sample] or Model[Sample] or a prepared sample or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((ObjectP[{Object[Sample], Model[Sample]}] | _String) | Automatic) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
Incubation
IncubationCondition
The type of incubation that defines the Temperature, Carbon Dioxide Percentage, Relative Humidity, Shaking Rate and Shaking Radius, under which the input cells are incubated. Custom incubation actively selects an incubator in the lab and uses a thread to incubate only the cells from this protocol for the specified Time. Selecting an IncubationCondition, through a symbol or an object, will passively store the cells for the specified time in a shared incubator, potentially with samples from other protocols. However, it will not consume a thread while the cells are inside the incubator. Currently, MammalianIncubation, BacterialIncubation, BacterialShakingIncubation, YeastIncubation, and YeastShakingIncubation are supported cell culture incubation conditions with shared incubators.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to a storage condition matching specified CellType, CultureAdhesion, Temperature, CarbonDioxide, RelativeHumidity, ShakingRate and ShakingRadius options, or set to Custom if no existing storage conditions can provide specified incubation condition options. If no Temperature, RelativeHumidity, CarbonDioxide, ShakingRate, or ShakingRadius are provided, automatically set based on the CellType and CultureAdhesion as described in the below table.
Pattern Description: Incubation Model or Incubation Type or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (((BacterialIncubation | YeastIncubation | Custom) | ObjectP[Model[StorageCondition]]) | Automatic) | Null
Temperature
Temperature at which the input cells are incubated. 30 Degrees Celsius and 37 Degrees Celsius are supported by default cell culture incubation conditions. Alternatively, a customized temperature can be requested with a dedicated custom incubator between 28 degrees Celsius and 80 degrees Celsius until the protocol is completed. See the IncubationCondition option for more information.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to match the Temperature field of specified IncubationCondition. If IncubationCondition is set to Custom, automatically set to 30 Celsius.
Pattern Description: Custom Temperature or Temperature or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: ((CellIncubationTemperatureP | RangeP[$MinCellIncubationTemperature, $MaxCellIncubationTemperature]) | Automatic) | Null
ColonyIncubationTime
The duration during which the colony samples are incubated inside of cell incubator before imaging.
Default Calculation: If PreparedSample is set to False, automatically set to the shorter time of 10 Hour or ten times the DoublingTime of the cells in the samples, with a minimum of 1 hour.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 hour and less than or equal to 72 hours or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (RangeP[1*Hour, $MaxCellIncubationTime] | Automatic) | Null
Analysis
MinReliableColonyCount
The smallest number of colonies that can be counted on a solid media plate to provide a statistically reliable estimate of the concentration of microorganisms in a sample. Below this number, the count is considered statistically unreliable and the result is typically referred to as "Too Few To Count" (TFTC).
Default Calculation: If PreparedSample is set to False, automatically set to 30, otherwise set to 1.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 100 in increments of 1.
Programmatic Pattern: RangeP[1, 100, 1] | Automatic
MaxReliableColonyCount
The largest number of colonies that can be counted on a solid media plate beyond which accurate counting becomes impractical and unreliable. This threshold is typically set at 300 colonies. When the number of colonies exceeds this limit, it is difficult to distinguish and count individual colonies accurately, and the result is typically referred as "Too Numerous To Count" (TNTC).
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 1000 in increments of 1.
Programmatic Pattern: RangeP[1, 1000, 1]
MinDiameter
The smallest diameter value from which colonies will be included in TotalColonyCounts in the data and analysis. The diameter is defined as the diameter of a circle with the same area as the colony.
Default Value: 0.5 millimeters
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0.2 millimeters and less than or equal to 10 millimeters or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | RangeP[$QPixMinDiameter, 10*Millimeter]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
MaxDiameter
The largest diameter value from which colonies will be included in TotalColonyCounts in the data and analysis. The diameter is defined as the diameter of a circle with the same area as the colony.
Default Value: 2 millimeters
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0.2 millimeters and less than or equal to 10 millimeters or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | RangeP[$QPixMinDiameter, 10*Millimeter]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
MinColonySeparation
The closest distance included colonies can be from each other from which colonies will be included in the data and analysis. The separation of a colony is the shortest path between the perimeter of the colony and the perimeter of any other colony.
Default Value: 0.2 millimeters
Pattern Description: Greater than 0 millimeters or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | GreaterP[0*Millimeter]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
MinRegularityRatio
The smallest regularity ratio from which colonies will be included in the data and analysis. The regularity ratio is the ratio of the area of the colony to the area of a circle with the colony's perimeter. For example, jagged edged shapes will have a longer perimeter than smoother ones and therefore a smaller regularity ratio.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | RangeP[0, 1]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
MaxRegularityRatio
The largest regularity ratio from which colonies will be included in the data and analysis. The regularity ratio is the ratio of the area of the colony to the area of a circle with the colony's perimeter. For example, jagged edged shapes will have a longer perimeter than smoother ones and therefore a smaller regularity ratio.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | RangeP[0, 1]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
MinCircularityRatio
The smallest circularity ratio from which colonies will be included in the data and analysis. The circularity ratio is defined as the ratio of the minor axis to the major axis of the best fit ellipse. For example, a very oblong colony will have a much larger major axis compared to its minor axis and therefore a low circularity ratio.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | RangeP[0, 1]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
MaxCircularityRatio
The largest circularity ratio from which colonies will be included in the data and analysis. The circularity ratio is defined as the ratio of the minor axis to the major axis of the best fit ellipse. For example, a very oblong colony will have a much larger major axis compared to its minor axis and therefore a low circularity ratio.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | RangeP[0, 1]) | Null
Index Matches to: Microscope data
Populations
The criteria used to group colonies together into a population to count. Criteria are based on the ordering of colonies by the desired feature(s): Diameter, Regularity, Circularity, Isolation, Fluorescence, and BlueWhiteScreen. For more information see documentation on colony population Unit Operations: Diameter, Isolation, Regularity, Circularity, Fluorescence, BlueWhiteScreen, MultiFeatured, and AllColonies under Experiment Principles section.
Default Calculation: If the Model[Cell] information in the sample object matches one of the fluorescent excitation and emission pairs of the colony picking instrument, Populations is set to Fluorescence. If BlueWhiteScreen is specified in ImagingStrategies, Populations is set to BlueWhiteScreen. Otherwise, Populations is set to All.
Pattern Description: Multiple Colony Populations or Single Colony Population.
Programmatic Pattern: (((Fluorescence | BlueWhiteScreen | Diameter | Isolation | Circularity | Regularity | All) | FluorescencePrimitiveP | BlueWhiteScreenPrimitiveP | DiameterPrimitiveP | IsolationPrimitiveP | CircularityPrimitiveP | RegularityPrimitiveP | AllColoniesPrimitiveP | MultiFeaturedPrimitiveP) | {((Fluorescence | BlueWhiteScreen | Diameter | Isolation | Circularity | Regularity | All) | FluorescencePrimitiveP | BlueWhiteScreenPrimitiveP | DiameterPrimitiveP | IsolationPrimitiveP | CircularityPrimitiveP | RegularityPrimitiveP | AllColoniesPrimitiveP | MultiFeaturedPrimitiveP)..}) | Automatic
Index Matches to: experiment samples
PopulationCellTypes
The cell type thought to represent the physiological characteristics defined in each of the Populations.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the cell type of the specified PopulationIdentities if it is a Model[Cell]. Otherwise, PopulationCellTypes is set to the cell type of the analyte or the cell model with the highest concentration from the input sample.
Pattern Description: CellType for single Colony Population or CellTypes for Multiple Colony Populations.
Programmatic Pattern: ((Bacterial | Yeast) | {(Bacterial | Yeast)..}) | Automatic
Index Matches to: experiment samples
PopulationIdentities
The cell constituent thought to represent the physiological characteristics defined in each of the Populations. If given as a string, a new Model[Cell] with the given name will be created with the type specified in option PopulationCellTypes and the current model of the given sample will be removed after the quantification step.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to the cell model of the analyte or the cell model if there is only one cell model in the Composition of the input sample, otherwise set to "Characterized Colony from <SampleID> #", and the protocol ID is always appended to the end of name string automatically at the time of model creation.
Pattern Description: CellIdentities for Multiple Colony Populations or CellIdentity for single Colony Population.
Programmatic Pattern: ((_String | ObjectP[{Model[Cell, Bacteria], Model[Cell, Yeast]}]) | {(_String | ObjectP[{Model[Cell, Bacteria], Model[Cell, Yeast]}])..}) | Automatic
Index Matches to: experiment samples
Incubation Repeat
IncubateUntilCountable
Indicates whether colony samples should undergo repeated cycles of incubation, imaging, and analysis until one of the following conditions is met: 1) The TotalColonyCounts from analyses are no longer increasing after surpassing the MinReliableColonyCount. 2) The TotalColonyCounts from analyses exceed the MaxReliableColonyCount. 3) A predetermined maximum incubation time is reached. The criteria for identifying colonies large enough to be counted can be set using the following options: MinDiameter, MaxColonySeparation, MinRegularityRatio, MaxRegularityRatio, MinCircularityRatio, and MaxCircularityRatio. Refer to Figure 3.2 for more information on colony identification criteria.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to True if PreparedSample is False.
Pattern Description: True or False or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (BooleanP | Automatic) | Null
NumberOfStableIntervals
The number of consecutive intervals during which the TotalColonyCounts remain stable (do not increase). For example, if the TotalColonyCounts (e.g. {200, 240, 240}) do not increase for the last two consecutive incubation intervals, the stable interval number is 1. This metric is used to determine whether all viable colonies have been counted when calculating Colony Forming Units (CFU). This stability indicates that the growth phase of the colonies has plateaued, ensuring an accurate count of all viable colonies present.
Default Calculation: Automatically set to 1 if IncubateUntilCountable is True.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 5 or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (RangeP[1, 5] | Automatic) | Null
MaxColonyIncubationTime
The maximum duration during which the colony samples are allowed to be incubated inside of cell incubator.
Default Calculation: If PreparedSample is set to False and IncubateUntilCountable is set to True, automatically set to the shorter time of 20 Hour or twenty times the DoublingTime of the cells in the samples, with a minimum of 2 hour. Otherwise set to the same value as IncubationTime if IncubateUntilCountable is set to False.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 2 hours and less than or equal to 72 hours or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (RangeP[2*Hour, $MaxCellIncubationTime] | Automatic) | Null
IncubationInterval
The duration during which colony samples are placed inside a cell incubator as part of repeated cycles of incubation, imaging, and analysis. Following this interval, the samples are moved out of the cell incubator and undergo imaging and analysis until all analyses return at least one value of TotalColonyCounts above the MinReliableColonyCount or until the MaxIncubationTime is reached.
Default Calculation: If IncubateUntilCountable is set to True, automatically set to the shorter time of 5 hours or five times the DoublingTime of the cells in the samples, with a minimum of 1 hour. Any time less than 1 hour is not sufficient to complete the cycle of setting up incubator and imaging instrument.
Pattern Description: Greater than or equal to 1 hour and less than or equal to 72 hours or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (RangeP[1*Hour, $MaxCellIncubationTime] | Automatic) | Null
Post Experiment
SamplesInStorageCondition
The non-default conditions under which the SamplesIn of this experiment should be stored after the protocol is completed. If left unset, SamplesIn will be stored according to their current StorageCondition.
Pattern Description: {AmbientStorage, EnclosedAmbientStorage, Refrigerator, Freezer, DeepFreezer, CryogenicStorage, YeastIncubation, YeastShakingIncubation, BacterialIncubation, BacterialShakingIncubation, MammalianIncubation, ViralIncubation, CrystalIncubation, AcceleratedTesting, IntermediateTesting, LongTermTesting, UVVisLightTesting} or Disposal or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Alternatives[SampleStorageTypeP | Disposal]) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples
SamplesOutStorageCondition
The non-default conditions under which any new samples generated by this experiment should be stored after the protocol is completed. If left unset, the new samples will be stored according to their Models' DefaultStorageCondition.
Pattern Description: {AmbientStorage, EnclosedAmbientStorage, Refrigerator, Freezer, DeepFreezer, CryogenicStorage, YeastIncubation, YeastShakingIncubation, BacterialIncubation, BacterialShakingIncubation, MammalianIncubation, ViralIncubation, CrystalIncubation, AcceleratedTesting, IntermediateTesting, LongTermTesting, UVVisLightTesting} or Disposal or Null.
Programmatic Pattern: (Null | (Alternatives[SampleStorageTypeP | Disposal])) | Null
Index Matches to: experiment samples